Difference between revisions of "Open Source WiFi Weather Station System"
From Microduino Wiki
(→Get and Configure Blynk) |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Outline== | ==Outline== | ||
*Project: Open Source WIFI Weather Station System.(ESP8266 connected to Blynk) | *Project: Open Source WIFI Weather Station System.(ESP8266 connected to Blynk) | ||
| − | *Objective: To get temperature, humidity, light intensity and | + | *Objective: To get temperature, humidity, light intensity and PM2.5 at the weather station. |
| + | **Note: PM2.5 refers to atmospheric particulate matter (PM) that have a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers | ||
*Difficulty: Medium | *Difficulty: Medium | ||
*Time-consuming: 2-Hour | *Time-consuming: 2-Hour | ||
*Maker: Ray | *Maker: Ray | ||
| − | + | Introduction: | |
| − | * | + | *Read temperature, humidity, light intensity and PM2.5 data and display those data on the screen. |
*Upload the data to Blynk. | *Upload the data to Blynk. | ||
| − | * | + | *View data on phone anywhere using the Blynk app. |
| − | * | + | *Created by Microduino with Microduino components. |
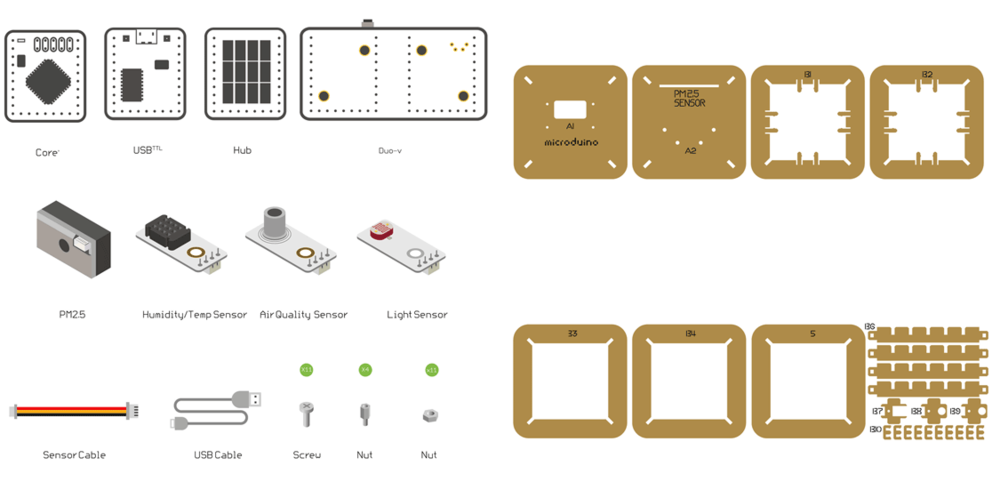
==Bill of Material== | ==Bill of Material== | ||
===Microduino Equipment=== | ===Microduino Equipment=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FEF9E7;" | ||
| + | |'''Note:''' Different revisions may contain different components. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Module||Number||Function | |Module||Number||Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-Core+]]||1||Core board | + | |[[Microduino-Core+]]||1|| Core board (Arduino) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-USBTTL]] ||1|| | + | |[[Microduino-USBTTL]] -OR- Microduino-USBTLL-C ||1|| Programmer for Core board |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-WIFI(ESP)]] ||1|| | + | |[[Microduino-WIFI(ESP)]] ||1|| WiFi communication module |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-Sensorhub]] ||1|| | + | |[[Microduino-Sensorhub]] ||1|| Connector Hub to connect sensors |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-Duo-h]] ||1||Extension board | + | |[[Microduino-Duo-h]] -OR- Microduino-Cube-S1 ||1|| Extension board |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Microduino-OLED]] ||1||Display | |[[Microduino-OLED]] ||1||Display | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
|Sensor||Number||Function | |Sensor||Number||Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Microduino-Temp&Hum]] ||1||Digital temperature and humidity sensor | + | |[[Microduino-Temp&Hum]] -OR- [[Sensor-Tem&Hum-S2]] ||1||Digital temperature and humidity sensor |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Microduino-Air Quality]] ||1||Air quality detector | |[[Microduino-Air Quality]] ||1||Air quality detector | ||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
|[[Microduino-Light]] ||1||Light-sensitive sensor | |[[Microduino-Light]] ||1||Light-sensitive sensor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |GP2Y1010AU0F ||1||PM2.5 sensor |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 62: | Line 65: | ||
|Shell ||1|| | |Shell ||1|| | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | [[File:weatherStationMatiralAll.png||1000px | + | [[File:weatherStationMatiralAll.png||1000px]] |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FEF9E7;" | ||
| + | |'''Note:''' Different revisions will contain different components. | ||
| + | Most noteable are: | ||
| + | *Duo-V will be replaced with a Microduino-Cube-S1. | ||
| + | *Humidity/TempSensor will be replaced with a Tem&Hum-S2. | ||
| + | |} | ||
==Principle of the Experiment== | ==Principle of the Experiment== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 82: | ||
| − | * | + | Other functions: |
| − | *Display on [[Microduino-OLED]] | + | *Use the [[Microduino-Core+]] to analyze and process sensor data. |
| − | *Connect the Weather Station with Blynk via [[Microduino-WIFI(ESP)]] | + | *Display data on the [[Microduino-OLED]]. |
| − | *Each sensor connects with [[Microduino-Sensorhub]] | + | *Connect the Weather Station with Blynk via [[Microduino-WIFI(ESP)]]. |
| − | + | *Each sensor connects with [[Microduino-Sensorhub]]. | |
==Get and Configure Blynk== | ==Get and Configure Blynk== | ||
Next, we'll learn how Microduino interacts with Blynk through the configuration process of the Weather Station. | Next, we'll learn how Microduino interacts with Blynk through the configuration process of the Weather Station. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Download the Blynk App=== |
| − | |||
| − | + | Visit the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store and download the '''Blynk''' app. | |
| − | + | You'll need to setup an account with Blynk before proceeding. Please use a valid e-mail as your authentication tokens will be sent to that e-mail. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Using the Blynk App== | ||
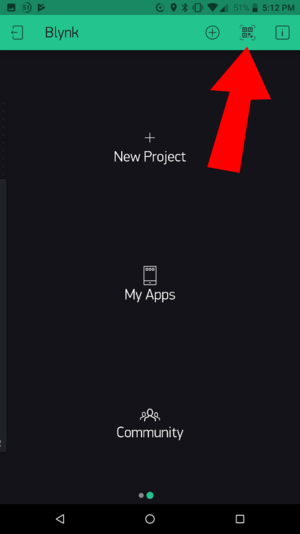
| − | + | *On the main screen of the Blynk app. Click on the '''QR code scanner''' to scan the Weather Station app. | |
| − | + | ::[[File:wws_qr_scan.png|300px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| + | *Scan the QR code below. | ||
| + | ::[[File:Wws_qr_code.png|300px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Once the project has loaded, click on '''Project Settings''' (nut icon). | ||
| + | ::[[File:wws_project_settings.png|300px]] | ||
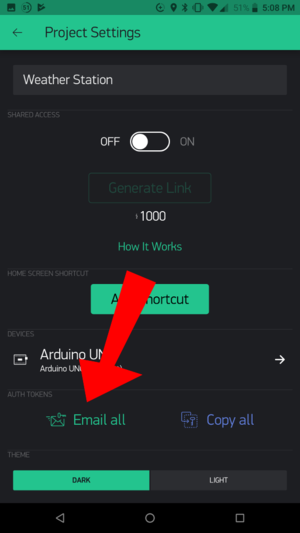
| − | + | *Under Auth Tokens, click on '''Email all'''. This will send the authentication token to your registered e-mail. Make note of this, as you will need this token later. | |
| − | + | ::[[File:wws_auth_token.png|300px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Click back to return to the Weather Station app. | ||
| + | ::[[File:Wws_weather_app.png|300px]] | ||
| + | ==Programming== | ||
| − | + | ===Software Setup=== | |
| − | + | Please follow the guide to ensure your software is correctly setup. The software is required to program the WiFi Weather Station. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Download the latest software for your operating system and follow the getting started guides: | ||
| + | {{Clickable software guide boxes}} | ||
| + | {{Clickable_headed_image_table_box_clear}} | ||
| + | ===Programming the Weather Station=== | ||
| + | *Stack '''[[Microduino-Core+]]''' and '''[[Microduino-USBTTL]]''' together. | ||
| + | *Connect '''[[Microduino-USBTTL]]''' with a USB cable. Connect the other end to the PC being used. | ||
| + | *Open the Arduino IDE for Microduino development environment. (Please refer to the [[#Software Setup]] section). | ||
| + | *Configure the software to upload to the Core+ module as follows: | ||
| + | **Tools > Board > '''Microduino/mCookie-device''' | ||
| + | **Tools > Processor > '''Microduino/mCookie-Core+ (644pa)@16M,5V''' | ||
| + | **Tools > Port > '''select the port''' (On MacOS, NOT the Bluetooth one). | ||
| + | *'''Download''' | ||
| + | **Code for Weather Station here: <big>'''[[File:WiFiWeatherStationV3.zip]]'''</big> | ||
| + | *Unzip the file. Under the software (Arduino IDE), go to '''File > Open...''' and navigate to the unzipped folder and open the '''WiFiWeatherStationV3.ino''' file. | ||
| + | *The sketch with multiple files will open. Click on the '''userDef.h''' tab. You'll need to configure the WiFi connection (2.4GHz networks, non 5GHz) with: | ||
| + | **'''SSID''' | ||
| + | **'''PASS''' (WiFi password) | ||
| + | **'''auth''' key as noted earlier in the Blynk app sent to you via e-mail. | ||
| + | **'''#define ENABLE WIFI''' | ||
| + | ***Uncommented: WiFi is enabled. (default) | ||
| + | ***Comment out: WiFi is disabled. (Add to 2 slashes to comment out: //#define ENABLE WIFI) | ||
| + | **'''#define ENABLE_FAHRENHEIT''' | ||
| + | ***Uncommented: Temperature is displayed in Fahrenheit units. (default) | ||
| + | ***Comment out: Temperature is displayed in Celsius units. (Add to 2 slashes to comment out: //#define ENABLE_FAHRENHEIT) | ||
| + | ::[[File:Wws_configuration.png|500px]] | ||
| + | *Click on the '''upload button''' (right arrow icon on the top left) to upload the program. | ||
| + | *The program will compile and upload. Once completed a upload successful message will appear on the bottom left. | ||
| − | + | ==Hardware Buildup== | |
| − | + | ===Step 1=== | |
| − | + | *Fixate [[Microduino-OLED]] and '''Structure-A1''' with screws. | |
| − | + | [[File:Waetherstep1.jpg||600px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| + | ===Step 2=== | ||
| + | *Assemble '''Structure-B1~B5''' with '''Structure-B6'''. | ||
| + | [[File:Waetherstep2.jpg||600px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Step 3=== | |
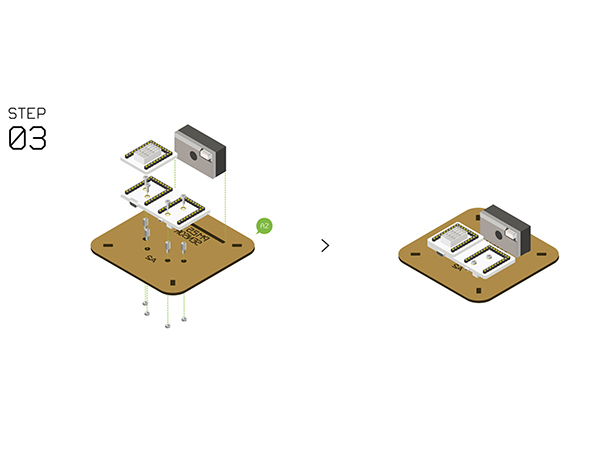
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FEF9E7;" | |
| − | + | |'''Note:''' Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a '''Duo-H''' or '''Cube-S1''' should be used. '''Duo-H''' is illustrated. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *Fixate [[Microduino-Duo-h]] / Microduino-Cube-S1 on '''Structure-A2''' with screws and nuts. | ||
| + | *Stack the following modules on [[Microduino-Duo-h]] / Microduino-Cube-S1. | ||
| + | **[[Microduino-Core+]] | ||
| + | **[[Microduino-USBTTL]] | ||
| + | **[[Microduino-WiFi]] | ||
| + | **[[Microduino-Sensorhub]] (on the very top of the stack) | ||
| + | *Attach the included adhesive strip onto the '''PM2.5 Sensor''' GP2Y1010AU0F, then to the base board. | ||
| + | [[File:Waetherstep3.jpg||600px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Step 4=== | |
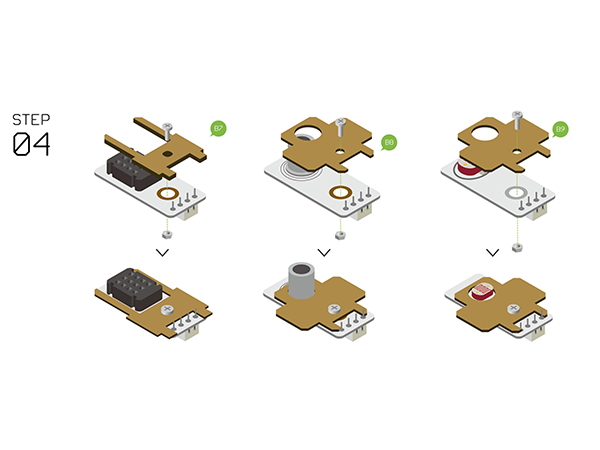
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FEF9E7;" | |
| − | + | |'''Note:''' Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a '''Temp&Hum''' or '''Tem&Hum-S2''' should be used. '''Temp&Hum''' is illustrated. | |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *Assemble the following sensors with '''Structure-B7, B8, B9'''. | ||
| + | **Temperature and humidity sensor ([[Microduino-Temp&Hum]] / Tem&Hum-S2) | ||
| + | **Air quality detector ([[Microduino-Air Quality]]) | ||
| + | **Light sensor ([[Microduino-Light]]) | ||
| + | [[File:Waetherstep4.jpg||600px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Step 5=== | |
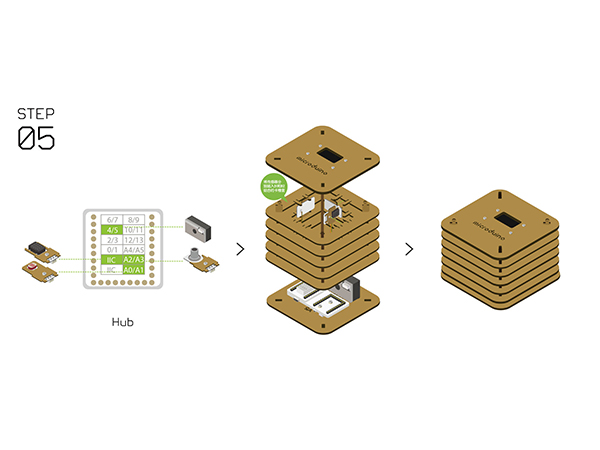
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="background-color:#FEF9E7;" | |
| − | + | |'''Note:''' Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a '''Temp&Hum''' or '''Tem&Hum-S2''' should be used. '''Temp&Hum''' is illustrated. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *Connect the sensors below to [[Microduino-Sensorhub]] using a '''connector wire'''. | ||
| + | **Temperature and humidity sensor ([[Microduino-Temp&Hum]] / Tem&Hum-S2) to a '''pin IIC'''. | ||
| + | **Air quality detector ([[Microduino-Air Quality]]) to '''pin A2/A3'''. | ||
| + | **Light sensor ([[Microduino-Light]]) to '''pin A0/A1'''. | ||
| + | **PM2.5 to '''pin 4/5'''. | ||
| + | **<span style="background:yellow">OLED screen to a '''pin IIC'''. (Not illustrated).</span> | ||
| + | *Refer to the picture below, stack all sensors on the slot of '''Structure-B1''' and '''Structure-B2'''. | ||
| + | *After that, connect '''Structure-A1''' and '''Structure-A2''' at the top and bottom of the system respectively. | ||
| + | [[File:Waetherstep5.jpg||600px]] | ||
| + | ===Step 6=== | ||
| + | *Complete the steps above, plug in a USB cable then fixate '''Structure-B0'''. Congratulations! You finished the buildup of the Weather Station. | ||
| − | + | ===Step 7=== | |
| − | + | *Power on the Weather Station. | |
| − | + | *The Weather Station will connect to the WiFi network. This may take a minute or so. | |
| − | * | + | *After connecting, the OLED screen will display the sensor data. |
| − | * | + | *If the data does not display, check the serial port in the IDE. It should display debugging information. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Step 8=== | ||
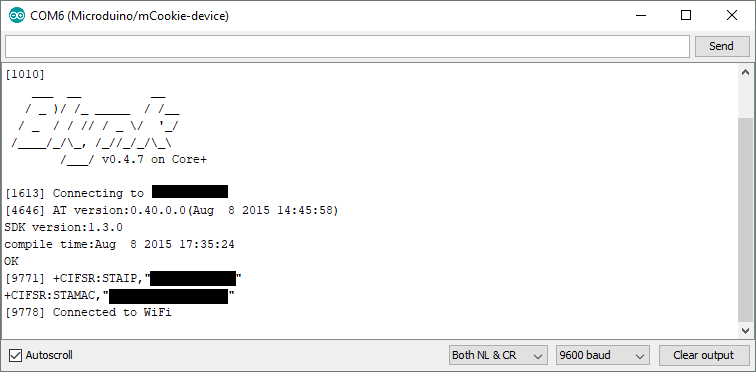
| + | *If the Weather Station successfully connect to the WiFi network. You can now view the data on the Blynk Phone app. | ||
| + | **WiFi Weather Station successfully connected to the WiFi network. | ||
| + | ::[[File:Wws_connected_to_wifi.png|Wws_connected_to_wifi.png]] | ||
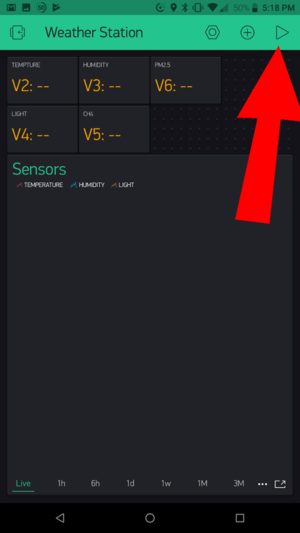
| − | + | *Return to your phone which is running Blynk. Open the Weather Station project. Click on Start (play icon). | |
| − | + | ::[[File:Wws_start_project.png|300px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
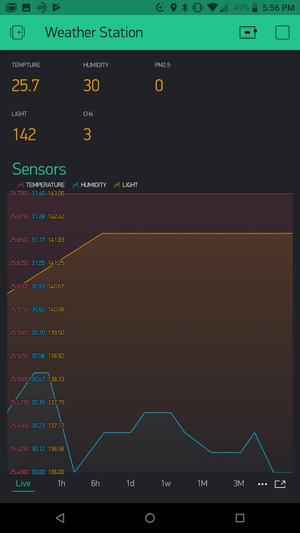
| − | + | *The sensor data should start streaming to the Blynk app. | |
| − | + | ::[[File:Wws_project_running.png|300px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | *The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| − | *Please make sure the verification code is configured right. | + | *Please make sure the verification code (blynk token) is configured right. |
| − | *Make sure your router runs normally, the SSID and password are correct. | + | *Make sure your router runs normally, the SSID and password are correct. |
| − | + | *Routers that require login, such as some public open networks that require accepting terms of service before internet is provide is not supported. As the WiFi module cannot interact with web pages. | |
| − | + | *If there is no display on the OLED (fuzzy screen) for more than 5 minutes, then the device may have issues connecting to the WiFi network. You may check the Serial port for debugging messages. Disable WiFi mode and see if the issue persists. | |
Latest revision as of 17:54, 23 April 2019
Contents
Outline
- Project: Open Source WIFI Weather Station System.(ESP8266 connected to Blynk)
- Objective: To get temperature, humidity, light intensity and PM2.5 at the weather station.
- Note: PM2.5 refers to atmospheric particulate matter (PM) that have a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers
- Difficulty: Medium
- Time-consuming: 2-Hour
- Maker: Ray
Introduction:
- Read temperature, humidity, light intensity and PM2.5 data and display those data on the screen.
- Upload the data to Blynk.
- View data on phone anywhere using the Blynk app.
- Created by Microduino with Microduino components.
Bill of Material
Microduino Equipment
| Note: Different revisions may contain different components. |
| Module | Number | Function |
| Microduino-Core+ | 1 | Core board (Arduino) |
| Microduino-USBTTL -OR- Microduino-USBTLL-C | 1 | Programmer for Core board |
| Microduino-WIFI(ESP) | 1 | WiFi communication module |
| Microduino-Sensorhub | 1 | Connector Hub to connect sensors |
| Microduino-Duo-h -OR- Microduino-Cube-S1 | 1 | Extension board |
| Microduino-OLED | 1 | Display |
| Sensor | Number | Function |
| Microduino-Temp&Hum -OR- Sensor-Tem&Hum-S2 | 1 | Digital temperature and humidity sensor |
| Microduino-Air Quality | 1 | Air quality detector |
| Microduino-Light | 1 | Light-sensitive sensor |
| GP2Y1010AU0F | 1 | PM2.5 sensor |
Other Equipment
| Equipment | Number | Function |
| Micro-USB cable | 1 | For program download and power supply |
| GP2Y1010AU0F | 1 | PM2.5 sensor |
| Screw | 7 | Fixate modules |
| Screwdriver | 1 | Fixate screws |
| Shell | 1 |
| Note: Different revisions will contain different components.
Most noteable are:
|
Principle of the Experiment
This Weather Station can detect data including:
- Temperature and humidity via Microduino-Temp&Hum
- Light intensity via Microduino-Light
- Air quality via Microduino-Air Quality
- PM2.5 via GP2Y1010AU0F
Other functions:
- Use the Microduino-Core+ to analyze and process sensor data.
- Display data on the Microduino-OLED.
- Connect the Weather Station with Blynk via Microduino-WIFI(ESP).
- Each sensor connects with Microduino-Sensorhub.
Get and Configure Blynk
Next, we'll learn how Microduino interacts with Blynk through the configuration process of the Weather Station.
Download the Blynk App
Visit the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store and download the Blynk app.
You'll need to setup an account with Blynk before proceeding. Please use a valid e-mail as your authentication tokens will be sent to that e-mail.
Using the Blynk App
- On the main screen of the Blynk app. Click on the QR code scanner to scan the Weather Station app.
- Scan the QR code below.
- Once the project has loaded, click on Project Settings (nut icon).
- Under Auth Tokens, click on Email all. This will send the authentication token to your registered e-mail. Make note of this, as you will need this token later.
- Click back to return to the Weather Station app.
Programming
Software Setup
Please follow the guide to ensure your software is correctly setup. The software is required to program the WiFi Weather Station.
Download the latest software for your operating system and follow the getting started guides:
Programming the Weather Station
- Stack Microduino-Core+ and Microduino-USBTTL together.
- Connect Microduino-USBTTL with a USB cable. Connect the other end to the PC being used.
- Open the Arduino IDE for Microduino development environment. (Please refer to the #Software Setup section).
- Configure the software to upload to the Core+ module as follows:
- Tools > Board > Microduino/mCookie-device
- Tools > Processor > Microduino/mCookie-Core+ (644pa)@16M,5V
- Tools > Port > select the port (On MacOS, NOT the Bluetooth one).
- Download
- Code for Weather Station here: File:WiFiWeatherStationV3.zip
- Unzip the file. Under the software (Arduino IDE), go to File > Open... and navigate to the unzipped folder and open the WiFiWeatherStationV3.ino file.
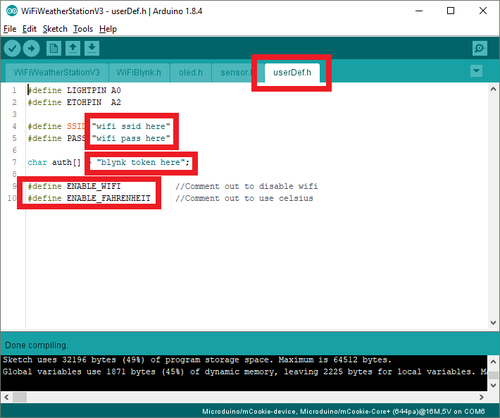
- The sketch with multiple files will open. Click on the userDef.h tab. You'll need to configure the WiFi connection (2.4GHz networks, non 5GHz) with:
- SSID
- PASS (WiFi password)
- auth key as noted earlier in the Blynk app sent to you via e-mail.
- #define ENABLE WIFI
- Uncommented: WiFi is enabled. (default)
- Comment out: WiFi is disabled. (Add to 2 slashes to comment out: //#define ENABLE WIFI)
- #define ENABLE_FAHRENHEIT
- Uncommented: Temperature is displayed in Fahrenheit units. (default)
- Comment out: Temperature is displayed in Celsius units. (Add to 2 slashes to comment out: //#define ENABLE_FAHRENHEIT)
- Click on the upload button (right arrow icon on the top left) to upload the program.
- The program will compile and upload. Once completed a upload successful message will appear on the bottom left.
Hardware Buildup
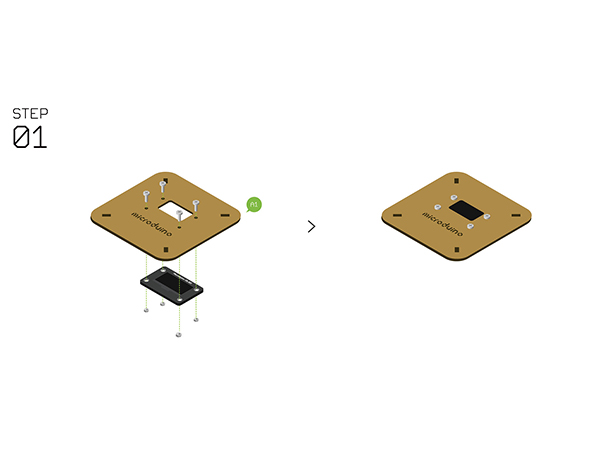
Step 1
- Fixate Microduino-OLED and Structure-A1 with screws.
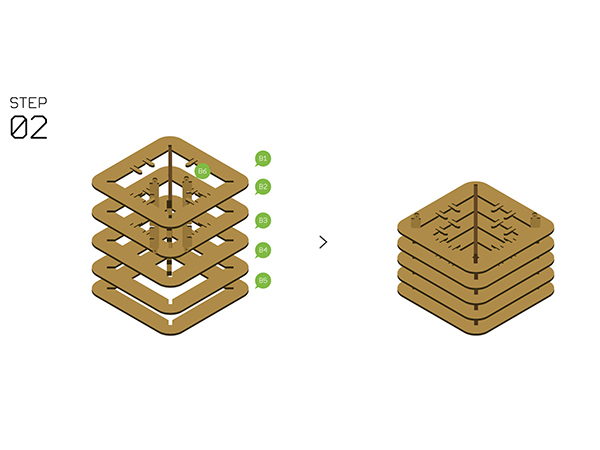
Step 2
- Assemble Structure-B1~B5 with Structure-B6.
Step 3
| Note: Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a Duo-H or Cube-S1 should be used. Duo-H is illustrated. |
- Fixate Microduino-Duo-h / Microduino-Cube-S1 on Structure-A2 with screws and nuts.
- Stack the following modules on Microduino-Duo-h / Microduino-Cube-S1.
- Microduino-Core+
- Microduino-USBTTL
- Microduino-WiFi
- Microduino-Sensorhub (on the very top of the stack)
- Attach the included adhesive strip onto the PM2.5 Sensor GP2Y1010AU0F, then to the base board.
Step 4
| Note: Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a Temp&Hum or Tem&Hum-S2 should be used. Temp&Hum is illustrated. |
- Assemble the following sensors with Structure-B7, B8, B9.
- Temperature and humidity sensor (Microduino-Temp&Hum / Tem&Hum-S2)
- Air quality detector (Microduino-Air Quality)
- Light sensor (Microduino-Light)
Step 5
| Note: Different revisions of this kit may contain different components. Either a Temp&Hum or Tem&Hum-S2 should be used. Temp&Hum is illustrated. |
- Connect the sensors below to Microduino-Sensorhub using a connector wire.
- Temperature and humidity sensor (Microduino-Temp&Hum / Tem&Hum-S2) to a pin IIC.
- Air quality detector (Microduino-Air Quality) to pin A2/A3.
- Light sensor (Microduino-Light) to pin A0/A1.
- PM2.5 to pin 4/5.
- OLED screen to a pin IIC. (Not illustrated).
- Refer to the picture below, stack all sensors on the slot of Structure-B1 and Structure-B2.
- After that, connect Structure-A1 and Structure-A2 at the top and bottom of the system respectively.
Step 6
- Complete the steps above, plug in a USB cable then fixate Structure-B0. Congratulations! You finished the buildup of the Weather Station.
Step 7
- Power on the Weather Station.
- The Weather Station will connect to the WiFi network. This may take a minute or so.
- After connecting, the OLED screen will display the sensor data.
- If the data does not display, check the serial port in the IDE. It should display debugging information.
Step 8
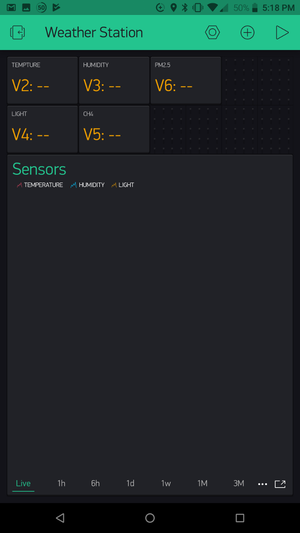
- If the Weather Station successfully connect to the WiFi network. You can now view the data on the Blynk Phone app.
- WiFi Weather Station successfully connected to the WiFi network.
- Return to your phone which is running Blynk. Open the Weather Station project. Click on Start (play icon).
- The sensor data should start streaming to the Blynk app.
Notes
- Please make sure the verification code (blynk token) is configured right.
- Make sure your router runs normally, the SSID and password are correct.
- Routers that require login, such as some public open networks that require accepting terms of service before internet is provide is not supported. As the WiFi module cannot interact with web pages.
- If there is no display on the OLED (fuzzy screen) for more than 5 minutes, then the device may have issues connecting to the WiFi network. You may check the Serial port for debugging messages. Disable WiFi mode and see if the issue persists.