Difference between revisions of "Microduino-Module CoreUSB"
(→Development) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
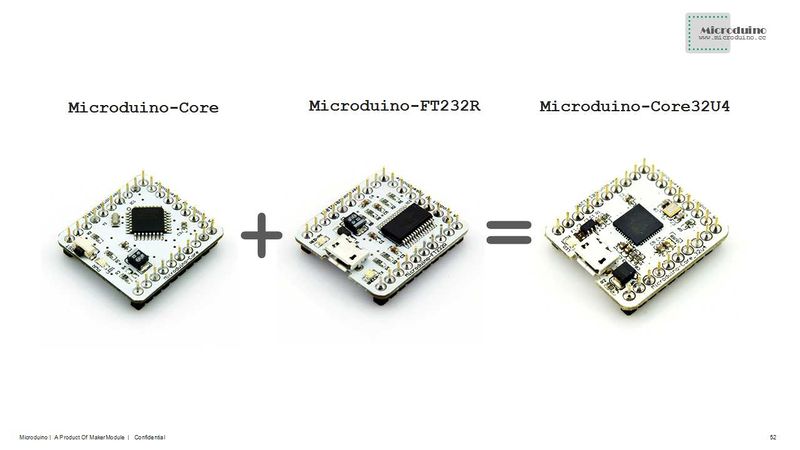
Microduino-CoreUSB 8-bit microcontroller development board with the ATMEGA32U4 series as the core,and it is a open-source controller module compatible with Arduino Leonardo. | Microduino-CoreUSB 8-bit microcontroller development board with the ATMEGA32U4 series as the core,and it is a open-source controller module compatible with Arduino Leonardo. | ||
| − | The difference between Microduino-CoreUSB and Microduino-core and Microduino-core+ is that the Microduino-CoreUSB contains a microcontroller and USB communication, equivalent to (Microduino-core + Microduino-USBTTL), and its pins conform to the | + | The difference between Microduino-CoreUSB and Microduino-core and Microduino-core+ is that the Microduino-CoreUSB contains a microcontroller and USB communication, equivalent to (Microduino-core + Microduino-USBTTL), and its pins conform to the Microduino specification. |
| − | Microduino uses java , the development environment of C language, same with Arduino. Players can use Arduino IDE, cooperating with software such as Flash or Processing , with Microduino and other electronic components,modules and sensors to make many funny interactive works. | + | Microduino uses java , the development environment of C language, same with Arduino. Players can use Arduino IDE, cooperating with software such as Flash or Processing, with Microduino and other electronic components,modules and sensors to make many funny interactive works. |
==Features== | ==Features== | ||
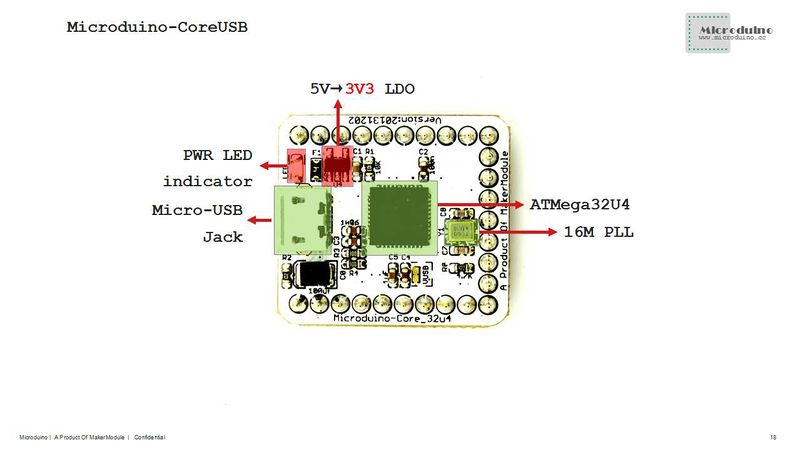
| − | *It contains microcontroller and USB communication, so you can directly download programs through the USB port, having no more need of Microduino- | + | *It contains microcontroller and USB communication, so you can directly download programs through the USB port, having no more need of Microduino-USBTTL; |
| − | *USB overcurrent | + | *USB overcurrent protection; |
*Small, cheap, stackable, and open; | *Small, cheap, stackable, and open; | ||
| − | *Open-source hardware circuit design, and programming development environment compatible with Arduino | + | *Open-source hardware circuit design, and programming development environment compatible with Arduino; |
| − | *Same with Arduino, Microduino can use ISP download way, to program to「bootloader」 | + | *Same with Arduino, Microduino can use ISP download way, to program to「bootloader」 flexibly; |
| − | *Unified Microduino interface specification, and abundant peripheral modules, can be connected and extended quickly, conveniently, and flexibly with other modules and sensors conforming to the Microduino interface | + | *Unified Microduino interface specification, and abundant peripheral modules, can be connected and extended quickly, conveniently, and flexibly with other modules and sensors conforming to the Microduino interface specification; |
*2.54 spacing Female Header interface is convenient to integrate into the hole plate. | *2.54 spacing Female Header interface is convenient to integrate into the hole plate. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
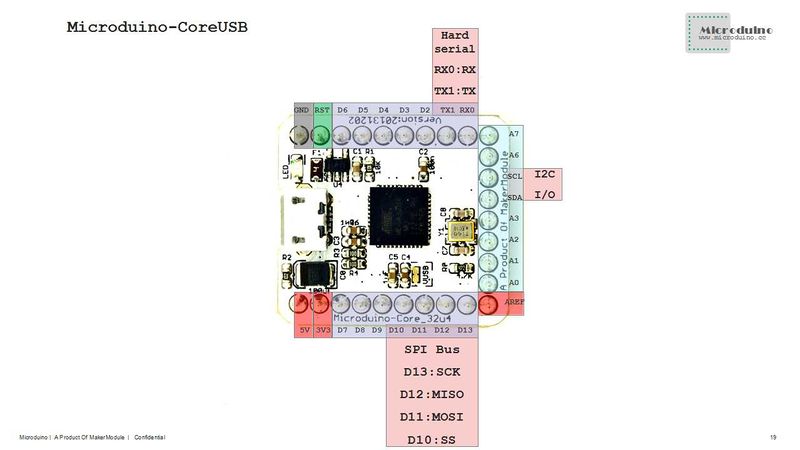
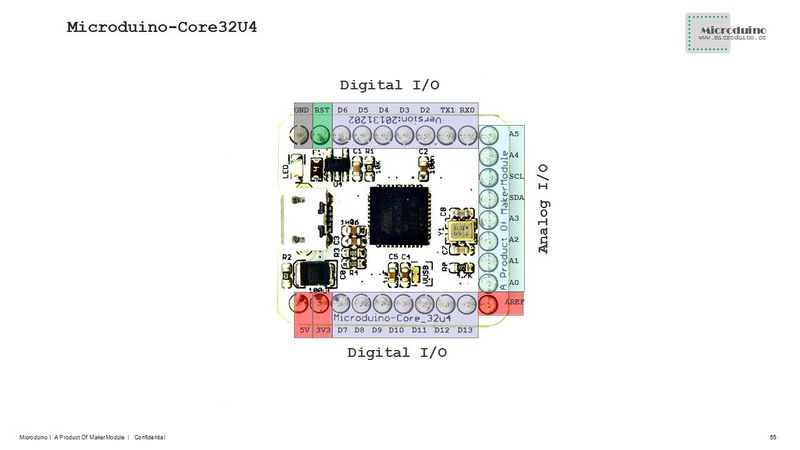
| − | * Digital I/O There are 22 digital input/output | + | * Digital I/O There are 22 digital input/output terminals: |
** Labeled on the module of D0~D13, and A0~A7. | ** Labeled on the module of D0~D13, and A0~A7. | ||
| − | * Analog I/O There are 10 analog input/ | + | * Analog I/O There are 10 analog input/output: |
| − | ** Labeled on thee module of A0,A1,A2,A3,A6,A7,D8(A8),D9(A9),D3(A10) and D4(A11) | + | ** Labeled on thee module of A0, A1, A2, A3, A6, A7, D8(A8), D9(A9), D3(A10) and D4(A11); |
| − | ** Each offers a 10-bit resolution( that is 0~1024). By default, the measurement range of the analog voltage is the value from GND to | + | ** Each offers a 10-bit resolution( that is 0~1024). By default, the measurement range of the analog voltage is the value from GND to VCC; |
** Please refer to'''[http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/AnalogRead analogRead()]''' function. | ** Please refer to'''[http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/AnalogRead analogRead()]''' function. | ||
| − | * PWM support. There are | + | * PWM support. There are 8: |
| − | ** Labeled on the module of respectively SCL,D3,D4,D5,D6,D7,D8 and D9. | + | ** Labeled on the module of respectively SCL, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9. |
** Please refer to'''[http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/AnalogWrite analogWrite()]''' function. | ** Please refer to'''[http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/AnalogWrite analogWrite()]''' function. | ||
| − | * Serial port support. There are | + | * Serial port support. There are 2: |
| − | ** USB virtual serial port | + | ** USB virtual serial port Serial; |
| − | ** Labeled on the module of Serial1[D0(RX),D1(TX)] | + | ** Labeled on the module of Serial1 [D0(RX), D1(TX)]. |
| − | * SPI support. There is | + | * SPI support. There is one: |
| − | ** Labeled on the module of D13(SCK),D12(MISO),D11(MOSI),D10(SS). | + | ** Labeled on the module of D13(SCK), D12(MISO), D11(MOSI), D10(SS). |
| − | * I2C support. There is | + | * I2C support. There is one: |
** Labeled on the module of SDA(D18),SCL(D19). | ** Labeled on the module of SDA(D18),SCL(D19). | ||
| − | * External interrupt support. There are | + | * External interrupt support. There are 5: |
** Labeled on the module of SCL(interrupt0), SDA(interrupt1), D0(interrupt2), D1(interrupt3), and D2(interrupt4). | ** Labeled on the module of SCL(interrupt0), SDA(interrupt1), D0(interrupt2), D1(interrupt3), and D2(interrupt4). | ||
** Please refer to'''[http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt attachInterrupt()]''' function. | ** Please refer to'''[http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt attachInterrupt()]''' function. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
* Support AREF end. | * Support AREF end. | ||
| − | *Instruction of the | + | *Instruction of the pins: |
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
Eagle PCB '''[[File:Microduino-core32U4.zip]]''' | Eagle PCB '''[[File:Microduino-core32U4.zip]]''' | ||
*The main components used in Microduino-core32U4. | *The main components used in Microduino-core32U4. | ||
| − | * | + | * MCU: '''[[File:ATmega32U4.zip]]''' |
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
* 1.Downloading programs to Microduino-CoreUSB , players need to use '''[[Microduino-USBTTL]]''' module. | * 1.Downloading programs to Microduino-CoreUSB , players need to use '''[[Microduino-USBTTL]]''' module. | ||
| − | * 2.The tutorial of setting the development environment and installing the driver is as | + | * 2.The tutorial of setting the development environment and installing the driver is as following: |
**'''[[Microduino Getting start]]''' | **'''[[Microduino Getting start]]''' | ||
* Program Microduino BootLoader | * Program Microduino BootLoader | ||
| − | ** If BootLoader is damaged, you need to use Arduino UNO or existing Microduino to program bootloader to the damaged Microduino | + | ** If BootLoader is damaged, you need to use Arduino UNO or existing Microduino to program bootloader to the damaged Microduino; |
| − | **Players can refer | + | **Players can refer to: '''[[Do you know how to use Arduino UNO to program bootloader to Microduino-Core?]]'''. |
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
* [https://www.microduino.cc/project Microduino Project cases] | * [https://www.microduino.cc/project Microduino Project cases] | ||
* [https://www.microduino.cc/wiki/index.php?title=Microduino_(Arduino%E5%85%BC%E5%AE%B9%E6%9D%BF%EF%BC%89%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B Microduino Applications tutorials] | * [https://www.microduino.cc/wiki/index.php?title=Microduino_(Arduino%E5%85%BC%E5%AE%B9%E6%9D%BF%EF%BC%89%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B Microduino Applications tutorials] | ||
| − | * [http://www.geek-workshop.com/thread-4558-1-1.html Microduino applications of the internet of things] | + | * [http://www.geek-workshop.com/thread-4558-1-1.html Microduino applications of the internet of things] [From geek-workshop.com] |
Latest revision as of 03:48, 4 August 2017
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
|
Microduino-CoreUSB 8-bit microcontroller development board with the ATMEGA32U4 series as the core,and it is a open-source controller module compatible with Arduino Leonardo. The difference between Microduino-CoreUSB and Microduino-core and Microduino-core+ is that the Microduino-CoreUSB contains a microcontroller and USB communication, equivalent to (Microduino-core + Microduino-USBTTL), and its pins conform to the Microduino specification. Microduino uses java , the development environment of C language, same with Arduino. Players can use Arduino IDE, cooperating with software such as Flash or Processing, with Microduino and other electronic components,modules and sensors to make many funny interactive works. Contents[hide]Features
Specification
DocumentEagle PCB File:Microduino-core32U4.zip
Development
Application
FAQ
PurchaseHistoryMap storageFrontageBackfaceVideo |