Outline
- Project:Microduino Mobile Bluetooth Controls the Color of RGB Lights Microduino
- Objective:The connection of Microduino BT and Microduino Core by cell phone to have Bluetooth communication and then to control the color of RGB lights.
- Difficulty:High
- Time-consuming:5 hours
- Maker:Microduino Studio-YLB
Principle
Mobile clients can simulate the color of the lights via three progress indicators which send the quantitative values obtained from simulation experiment to Microduino Core via BT. Thus, we can easily control the color of RGB lights by calculating since we get both the simulated values and analogWrite(). In order to have a better control experience, we need to connect pins of RGB lights to those of PMW(3、5、6、11) . Since both Microduino BT and Microduino Core adopt soft serial port for communication, we can't connect RGB lights to pins (9,10). Otherwise, data chaos may appear.
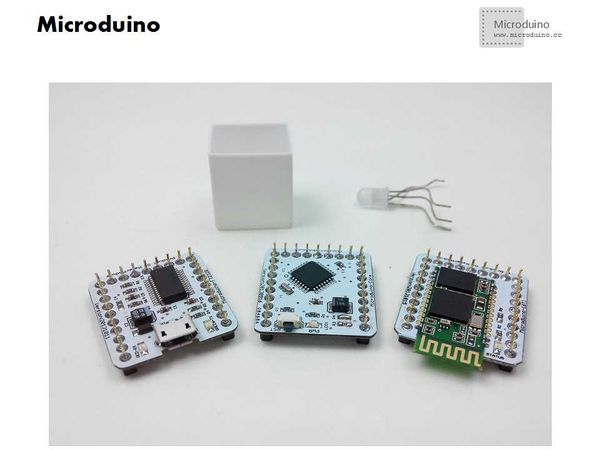
Bill of Materials
| Modules |
Number |
Function
|
| Microduino-Core |
1 |
Core module
|
| Microduino-FT232R |
1 |
Download program
|
| Microduino BT(2.1) |
1 |
Bluetooth communication
|
| RGB lights |
1 |
For display
|
| USB cable |
1 |
For power supply and program download
|
| Small 3D print box |
1 |
For beauty
|
Document
Android client: File:Microduino RGB.zip
Notice:Make sure your BT is the 2.1 version since Android client-side is only suitable for 2.1 BT temporarily
Program Test:
https://github.com/Microduino/Microduino_Tutorials/commit/46ebefd3f9739ccbede60e72d4463f998a33590f
Debugging
- Step 1:Prepare all equipments
- Step 2:Make sure your BT serial method.
Using soft serial port (9,10) for program test.
- If you adopt serial port (2,3)
- And you use Core, please change “SoftwareSerial mySerial(9, 10);”to“SoftwareSerial mySerial(2, 3); ”
- Or if you use Core+, you need to change “mySerial” of loop to “Serial1”.
- If you adopt serial port (0,1)
- You need to change “mySerial” of loop to “Serial1”.and can’t fold BT in the download, or the serial ports will conflict.
- Step 3:Build a Circuit
- Overlay modules available
- Make sure common anode RGB pins
- The longest pin is positive or the widest one when you look at the RGB light in the head. Here no electric resistance is adopted and the pin will be connected to 3.3V.
- Players can directly measure the corresponding color of the other three pins through a multimeter or a module. And then connect the pins correspondingly.
- Step 4:Download test program and open it.
- First, make sure your BT serial port, which can refer to step 2.
- Make sure the RGB lights are of common anode. If not, you need to:
- Change the solution:The longest pin refers to negative and meanwhile, you need to connect it to GND.
- Change program: you need to change analogWrite(); eg: To convert “analogWrite(6, 255 - red);”to “analogWrite(6, red);”
- Step 5:After that, you need to compile program and then download .
- Step 6:Download Android client-side, decompress, install and open it.
- Step 7:Search equipments and connect.
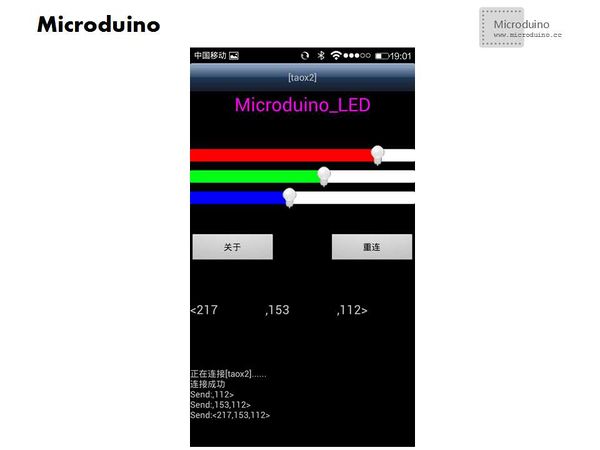
- Step 8:If the connection goes well, then the lights can be easily controlled by mobile Bluetooth. Otherwise, you have to reconnect. After several times of failed connection, you can either power down and reset the system, or just shut off the client-side and restart.
Result
In virtue of Microduino, you can successfully control RGB lights through cellphone
Notice
- Make sure the serial port of BT
- Figure out whether the RGB lights are of common anode or common cathode
- Pay attention to the connection method of RGB lights. If you find errors occur among color progress indicators and their corresponding RGB lights, you can also change pins of “analogWrite();” and make it right.
Video
http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNzAzNzAzMjQ4.html
|