|
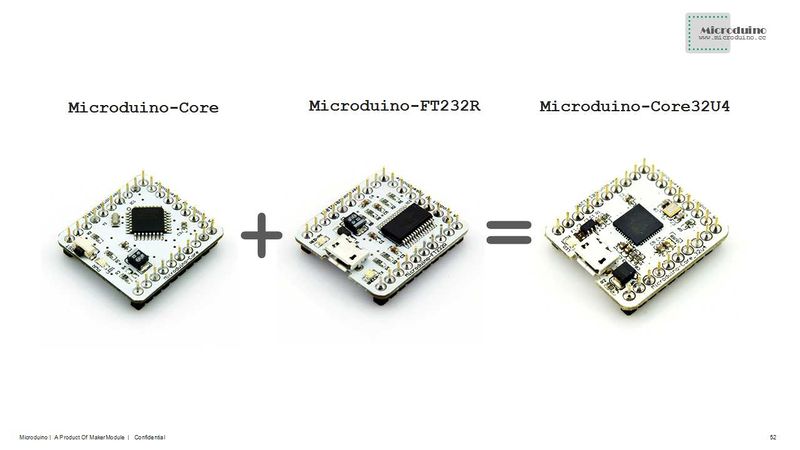
Microduino CoreUSB module uses the ATMEGA32U4 series 8-bit MCU as the core, which is an open source and Arduino Leonardo compatible controller module.
The difference between Microduino-CoreUSB and Microduino-Core/Microduino-Core+ is that it contains the microcontroller and USB communication. Its pin conforms to Microduino specification.
Microduino CoreUSB use the same Java/C development environment with Arduino. The player can use Arduino IDE and with other software Flash or Processing to do the development. Also can use Microduino and other electronic components, modules, sensors, make a lot of interesting product.
Features
- Contain the microcontroller and USB interface so that you can download programs via the interface and need no Microduino-USBTTL anymore;
- USB over-current protection;
- Small, cheap and stackable with open platform;
- With open source hardware circuit design, it is compatible with the Arduino IDE for programming;
- Adopt ISP download mode, easy for burning bootloader;
- With uniform Microduino interface standard and rich peripheral modules, it can have an easy and flexible connection with other Microduino modules and sensors.
- 2.54mm (0.1 inch) pin pitch, compatible to bread board and pegboards.
Specification
| Flash |
32 KB(ATMEGA32U4). 4KB for bootstrap program.
|
| SRAM |
2.5 KB(ATMEGA32U4)
|
| EEPROM |
1 KB(ATMEGA32U4)
|
| Frequency |
16 MHz
|
- 22 digital I/O ports:
- In the module, it is marked with D0~D13 and A0~A7.
- 10 analog I/O ports:
- In the module, it is marked with A0, A1, A2, A3, A6, A7, D8(A8), D9(A9), D3(A10) and D4(A11).
- Each analog input port offers 10-bit resolution(namely, 0-1024). The analog voltage range is from GND to VCC by default.
- For more information, please refer to: analogRead() function.
- PWM support:
- In the module, it is marked with SCL, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9 respectively.
- For more information, please refer to:analogWrite().
- Serial port support:
- Virtual USB Serial;
- In the module, it is marked with Serial1[D0(RX) and D1(TX)].
- Support SPI:
- In the module, it is marked with D13(SCK), D12(MISO), D11(MOSI) and D10(SS).
- Support I2C:
- In the module, it is marked with SDA(D18) and SCL(D19).
- External interruption support:
- In the module, it is marked with SCL(interrupt0), SDA(interrupt1), D0(interrupt2), D1(interrupt3) and D2(interrupt4).
- For more information, please refer to:attachInterrupt().
- Support ISP download function.
- Support AREF.
| Pin
|
Original Pin Name
|
Map Pin Name
|
Digital Pin
|
Analog Pin
|
interrupt
|
PWM
|
Serial
|
SPI
|
I2C
|
Power
|
| 1 |
VCC |
+5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+5V
|
| 2 |
VCC |
+3V3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+3.3V
|
| 3 |
(OC0A/OC1C/#RTS)PB7 |
D7 |
D7 |
|
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
(OC1B/0C4B/ADC13)PB6 |
D8 |
D8 |
A8 |
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
(OC1A/#OC4B/ADC12)PB5 |
D9 |
D9 |
A9 |
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
(SS)PB0 |
D10 |
D10 |
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
|
| 7 |
(PDI/MOSI)PB2 |
D11 |
D11 |
|
|
|
|
MOSI |
|
|
| 8 |
(PDO/MISO)PB3 |
D12 |
D12 |
|
|
|
|
MISO |
|
|
| 9 |
(SCK)PB1 |
D13 |
D13 |
|
|
|
|
SCK |
|
|
| 10 |
AREF |
AREF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
(ADC7/TDI)PF7 |
A0 |
D14 |
A0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
(ADC6/TDO)PF6 |
A1 |
D15 |
A1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
(ADC5/TMS)PF5 |
A2 |
D16 |
A2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
(ADC4/TCK)PF4 |
A3 |
D17 |
A3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
(SDA/INT1)PD1 |
SDA |
D18 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
SDA |
|
| 16 |
(OC0B/SCL/INT0)PD0 |
SCL |
D19 |
|
0 |
yes |
|
|
SCL |
|
| 17 |
(ADC1)PF1 |
A6 |
D20 |
A6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
(ADC0)PF0 |
A7 |
D21 |
A7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
(RXD1/AIN1/INT2)PD2 |
D0 |
D0 |
|
2 |
|
1(RX) |
|
|
|
| 20 |
(TXD1/INT3)PD3 |
D1 |
D1 |
|
3 |
|
1(TX) |
|
|
|
| 21 |
(INT6/AIN0)PE6 |
D2 |
D2 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
(T1/#OC4D/ADC9)PD6 |
D3 |
D3 |
A10 |
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
(T0/OC4D/ADC10)PD7 |
D4 |
D4 |
A11 |
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
(OC3A/#OC4A)PC6 |
D5 |
D5 |
|
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
(ICP3/CLK0/OC4A)PC7 |
D6 |
D6 |
|
|
yes |
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
RESET |
RST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
GND |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GND
|
 Microduino-Core32U4-Pinout 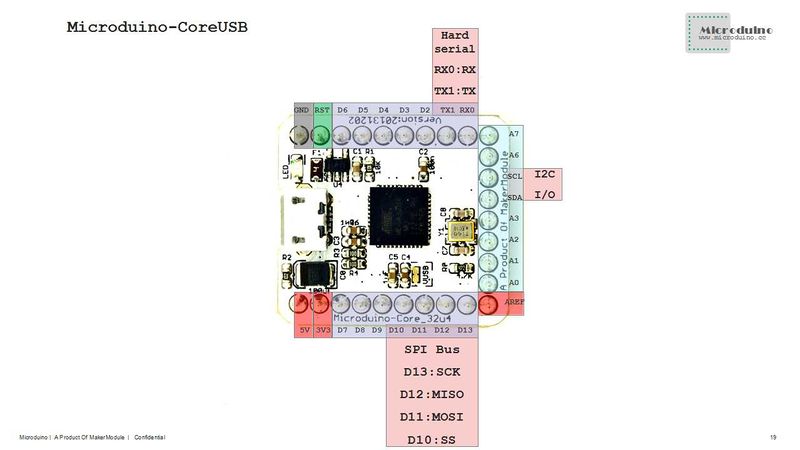 Microduino-Core32U4-Pinout 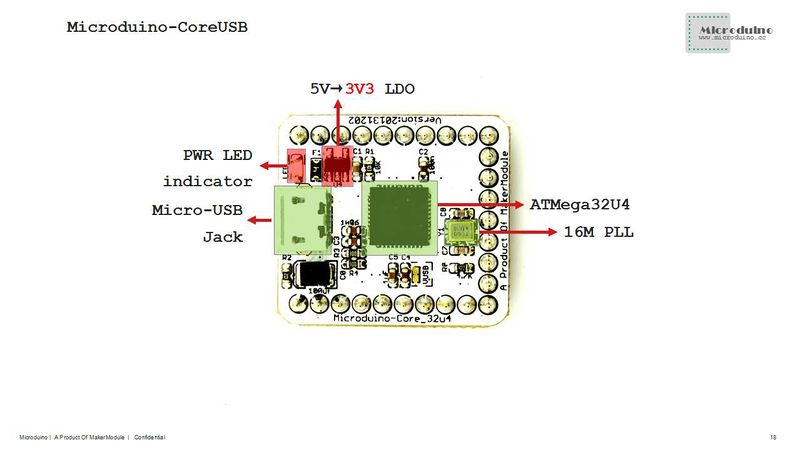 Microduino-Core32U4-Pinout 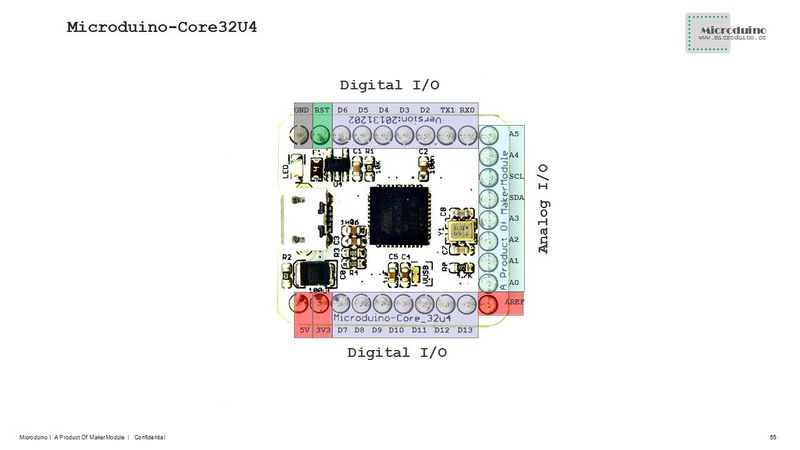 Microduino-Core32U4-Pinout Document
Eagle PCB File:Microduino-core32U4.zip
- Main components used in Microduino-CoreUSB
Development
- Configure Microduino development environment
- 1. Usage Arduino IDE:Microduino CoreUSB uses the same IDE development environment with Arduino, please download Arduino IDE firstly 【Arduino IDE Download】.
Detailed introduction for Arduino IDE, please refer to the tutorial. The player can use Arduino IDE and with other software Flash or Processing to do the development. Also can use Microduino and other electronic components, modules, sensors, make a lot of interesting product.
- 2. Use Arduino IDE to do the Microduino programing:Player need download Microduino support package for Arduino IDE firstly, and copy to corresponding folder.【Local download】 Player can refer the tutorial to configure the Arduino IDE.
- 3. Download program to Microduino-CoreUSB
Burn Microduino BootLoader
If the player was a Microduin CoreUSB empty board, you need to use the Arduino UNO or another Microduino to burn bootloader for another piece of Microduino empty board. Player can refer to the tutorial "Do you know how to use the Arduino UNO to burn bootloader for Microduino Core?
Various version's Microduino-Core uses different bootloader. Initial bootloader optiboot is designed for ATmegaX8 series, which occupies only 512 bytes flash.
Application
FQA
- Can this module work with Microduino-GPRS/GSM module?
Bug
History
Picture
Front
 Microduino-Core32U4 Front Back
Video
|






