Difference between revisions of "The Use of Joystick Sensor"
From Microduino Wiki
(Created page with " {| style="width: 800px;" |- | ==Purpose== This tutorial will show you how to use Microduino Joystick. ==Equipment== *'''Microduino-CoreUSB''' *'''Microduino-Joystic...") |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | == | + | ==Outline== |
| − | + | The Microduino Joystick sensor is two analog output devices in one. There are resistors on the X-axis and Y-axis that each output an analog value corresponding to the position of the joystick on that axis. | |
| + | This sensor is great for controlling projects, especially ones that move. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Specification== |
| − | * | + | *Electrical Specifications |
| − | * | + | **Analog Output Device |
| − | * | + | **Analog Output: 0-1023 (with Microduino Core modules) |
| − | + | *Technical Specifications | |
| + | **Analog Output Corresponding to X and Y-axis displacement | ||
| + | *Dimensions | ||
| + | **Switch: 17mm x 17mm | ||
| + | **Board: 20mm x 24mm | ||
| + | *Connection Interface | ||
| + | **Pins: Signal 1 (X-Axis), Signal 2 (Y-Axis), VCC (power) and GND (ground) | ||
| + | **Must be connected to analog capable ports (A0-A7) | ||
| + | [[File:Joystick-line.jpg|center|400px]] | ||
| + | ==Development== | ||
| + | ===Equipment=== | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Module||Number||Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[mCookie-CoreUSB]]||1||Core board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[mCookie-Hub]]||1||Sensor pin board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Microduino-Joystick]]||1||Joystick sensor | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *Other Hardware Equipment | ||
| + | **One USB cable | ||
| + | [[File:module-joystick.jpg|600px|center]] | ||
| − | * | + | ===Preparation=== |
| − | * | + | *Setup 1: Connect Microduino-Joystick and the Hub 's A0 and A1 analog ports. |
| + | [[file:mCookie-joystick.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
| + | *Setup 2: Stack the CoreUSB, Hub and Light together and then connect them to the computer with a USB cable. | ||
| + | [[file:mCookie-joystick.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Experiment: Detect Analog Joystick Value === |
| − | + | *Open Arduino IDE and copy the following code into IDE. | |
| + | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
| + | #define Pin_X A1 | ||
| + | #define Pin_Y A0 | ||
| − | + | void setup() { | |
| + | Serial.begin(9600); //Serial initializing | ||
| + | pinMode(Pin_X,INPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(Pin_Y,INPUT); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | void loop() { | |
| + | int sensorValueX = analogRead(Pin_X); //X-axis input | ||
| + | int sensorValueY = analogRead(Pin_Y); //Y-axis input | ||
| + | Serial.print("ValueX:"); | ||
| + | Serial.print(sensorValueX); | ||
| + | Serial.print(","); | ||
| + | Serial.print("ValueY:"); | ||
| + | Serial.println(sensorValueY); | ||
| + | delay(100); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
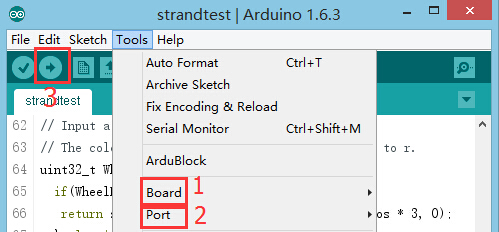
| + | * Select the right board from Tools→Serial Port in Arduino IDE and download the program. [[file:upload.JPG|500px|center]] | ||
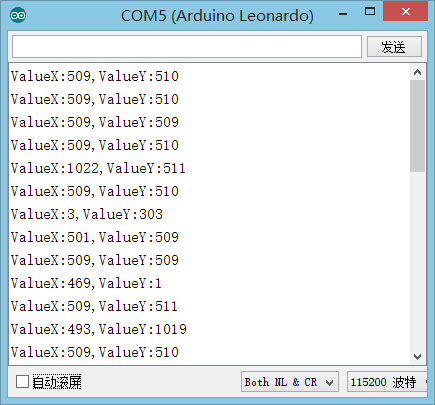
| + | * After the download, you can open the serial monitor. The displayed note reflects the current displacement analog values on both X-and Y-axis. | ||
| + | [[file:mCookie-pir-res.JPG|500px|center]] | ||
| + | *Result | ||
| + | **The right shift value decrease on the X-axis, close to zero while the left shift value increases and gets close to 1,023. | ||
| + | ** The top shift value decrease on the Y-axis, close to zero while the downward shift value increases and gets close to 1,023. | ||
| + | ===Program Debugging=== | ||
| + | *Use"analogRead(XX);" to read sensor's input analog value and judge the displacement on both the X-axis and Y-axis. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Application== |
| − | + | *To control object movement in two-dimensional space. | |
| − | + | *Game joystick | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Video== | ==Video== | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:44, 30 September 2016
ContentsOutlineThe Microduino Joystick sensor is two analog output devices in one. There are resistors on the X-axis and Y-axis that each output an analog value corresponding to the position of the joystick on that axis. This sensor is great for controlling projects, especially ones that move. Specification
DevelopmentEquipment
Preparation
Experiment: Detect Analog Joystick Value
#define Pin_X A1
#define Pin_Y A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Serial initializing
pinMode(Pin_X,INPUT);
pinMode(Pin_Y,INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValueX = analogRead(Pin_X); //X-axis input
int sensorValueY = analogRead(Pin_Y); //Y-axis input
Serial.print("ValueX:");
Serial.print(sensorValueX);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ValueY:");
Serial.println(sensorValueY);
delay(100);
}
Program Debugging
Application
Video |