Difference between revisions of "Colored LED"
From Microduino Wiki
(formatting) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*Ultra low power and ultra long life. | *Ultra low power and ultra long life. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Materials== |
| − | |||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
[[File:color_led-module.jpg|center|600px]] | [[File:color_led-module.jpg|center|600px]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Instructions== |
| + | |||
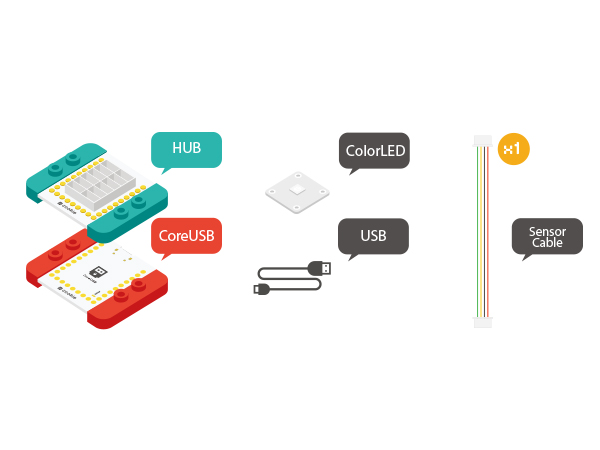
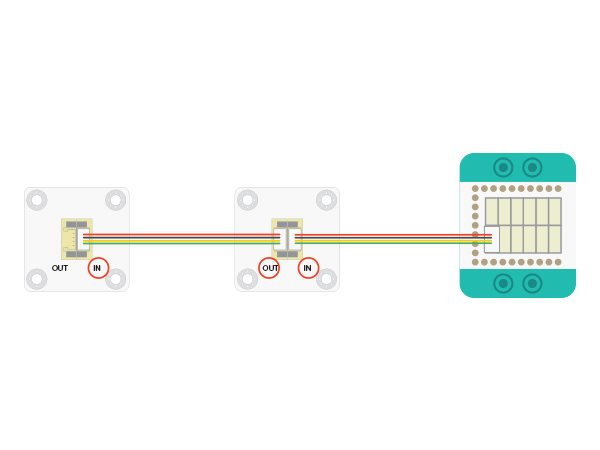
*Setup 1:Connect the '''IN''' port on the back of the Color LED with the D6 port of the Hub. (D6 is the LED control pin, which can be freely changed by users.) | *Setup 1:Connect the '''IN''' port on the back of the Color LED with the D6 port of the Hub. (D6 is the LED control pin, which can be freely changed by users.) | ||
[[file:mCookie-strandtext-sensor.JPG|600px|center]] | [[file:mCookie-strandtext-sensor.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[file:mCookie-strandtext-pc.JPG|600px|center]] | [[file:mCookie-strandtext-pc.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
| − | + | ==Experiment One: Get the Light Brighten == | |
The LED will change color between red, green, and blue every 500ms. <br> | The LED will change color between red, green, and blue every 500ms. <br> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
**Users can change the color of the LED by adjusting the RGB values. | **Users can change the color of the LED by adjusting the RGB values. | ||
| − | + | ==Experiment Two: Breathing Light == | |
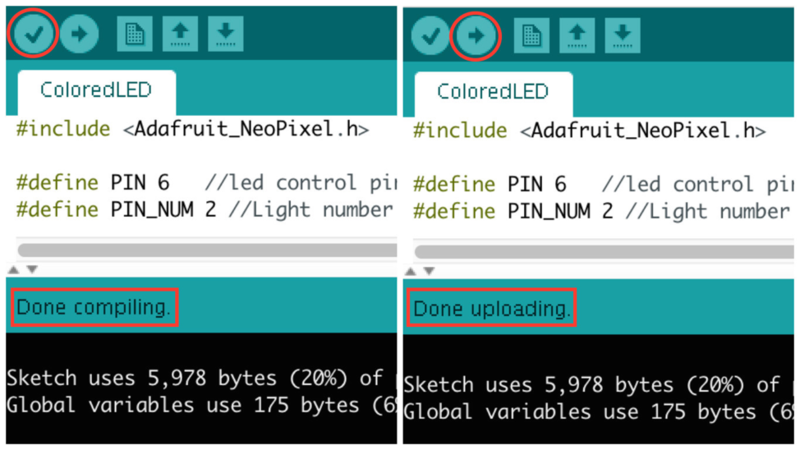
*Open Arduino IDE and copy the following code into IDE. | *Open Arduino IDE and copy the following code into IDE. | ||
<source lang="cpp"> | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
*In result, the red, green and blue lights "breath" in loop. | *In result, the red, green and blue lights "breath" in loop. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Program Debugging=== |
*“rainbowCycle( int r, int g, int b, uint8_t wait)” - Function Description: | *“rainbowCycle( int r, int g, int b, uint8_t wait)” - Function Description: | ||
**r:(0-255)。 | **r:(0-255)。 | ||
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
Additional Specs: | Additional Specs: | ||
[[File:ws2812.pdf]] | [[File:ws2812.pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 15 August 2016
ContentsOutlineMicroduino-Color LED is a colored LED light with an built-in IC control chip, which can be cascaded arbitrarily. With only one I/O port, you can control all the lights. Each light can be controlled separately. Features
Materials
Instructions
Experiment One: Get the Light BrightenThe LED will change color between red, green, and blue every 500ms.
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 6 //led control pin
#define PIN_NUM 2 //Light number allowed
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(PIN_NUM, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show();
}
void loop() {
colorWipe(strip.Color(255, 0, 0), 500); // The first light goes read and after 500ms, the second light will go red.
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 255, 0), 500); // The first light goes read and after 500ms, the second light will go green.
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 255), 500); // The first light goes read and after 500ms, the second light will go blue.
}
// Fill the dots one after the other with a color
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
//Let each light turn to a specific color in loop. "C" indicates color; "wait" represents the time duration of each light .
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
delay(wait);
}
}
Program Debugging
Experiment Two: Breathing Light
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 6 //LED light control pin
#define PIN_NUM 2 //LED light number allowed
#define val_max 255
#define val_min 0
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(PIN_NUM, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show();
}
void loop() {
rainbowCycle( 255, 0, 0, 10);//Red breathing
rainbowCycle( 0, 255, 0, 10);//Green breathing
rainbowCycle( 0, 0, 255, 10);//Blue breathing
}
void colorSet(uint32_t c) {
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
}
strip.show();
}
void rainbowCycle( int r, int g, int b, uint8_t wait) {
for (int val = 0; val < 255; val++)
{
colorSet(strip.Color(map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, r), map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, g), map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, b)));
delay(wait);
}
for (int val = 255; val >= 0; val--)
{
colorSet(strip.Color(map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, r), map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, g), map(val, val_min, val_max, 0, b)));
delay(wait);
}
}
Program Debugging
Specifications
Additional Specs: File:Ws2812.pdf
Application
|