Difference between revisions of "Lesson 3--Microduino "Button Controlled LED""
From Microduino Wiki
(→Program) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| | | | ||
==Objective== | ==Objective== | ||
| − | The first two | + | The first two lessons showed you how to use software to control the LED directly. If we add a button |
| − | to control the LED light, then | + | to control the LED light, then we can combine the use of both hardware and software. |
| − | + | Previously, we used Microduino I/O port as the output to control the LED. So if we want to use a button, | |
| − | how | + | how would we monitor when it is pressed? |
| − | + | In this lesson, we will use a button as an example to show how to use Microduino as an input. | |
| − | |||
==Equipment== | ==Equipment== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
*'''[[Microduino-FT232R]]''' | *'''[[Microduino-FT232R]]''' | ||
*Other hardware equipment | *Other hardware equipment | ||
| − | ** | + | **1x Box of breadboard jumper wires |
| − | **Breadboard | + | **1x Breadboard |
| − | **LED Light- | + | **1x LED (Light-Emitting Diode) |
| − | **220ohm resistor | + | **1x 220ohm resistor |
| − | **Button | + | **1x Button |
| − | **USB Data cable | + | **1x USB Data cable |
==Button== | ==Button== | ||
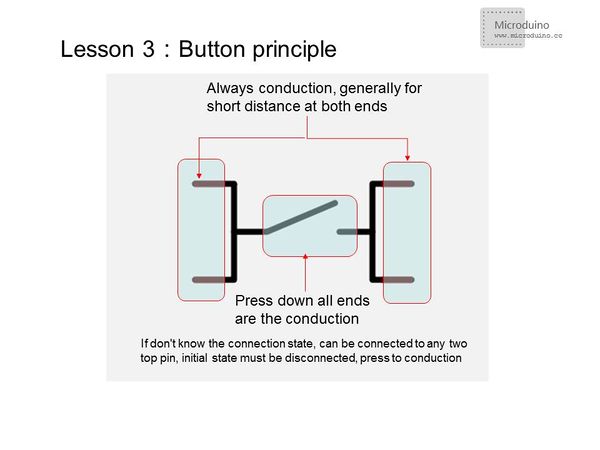
*Button principle | *Button principle | ||
[[File:button.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | [[File:button.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | |||
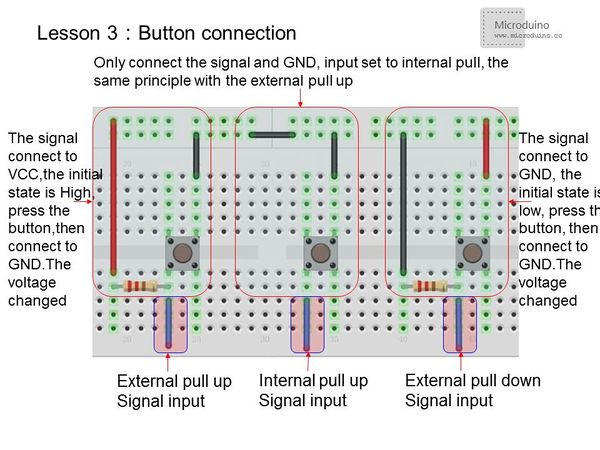
*Button connection | *Button connection | ||
[[File:button connection.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | [[File:button connection.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | ||
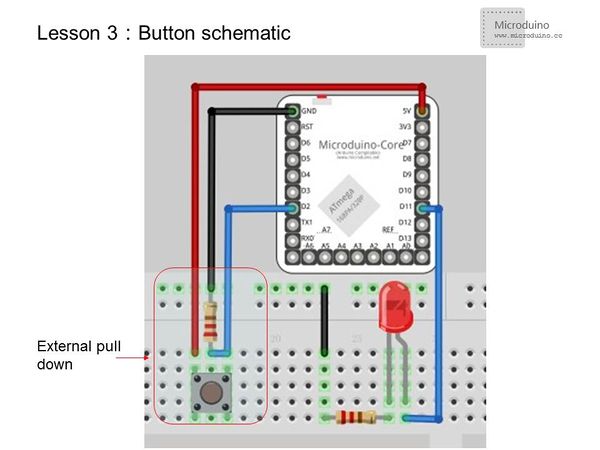
| − | == | + | ==Experiment Schematic== |
[[File:button schematic.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | [[File:button schematic.jpg|600px|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | Using external pulldown | + | Using the external pulldown method, when the button is unpressed, the input to D2 is "LOW". When pressed, it is "HIGH". |
| − | |||
==Program== | ==Program== | ||
| − | *LED | + | *LED is on while button is pressed down |
<source lang="cpp"> | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 41: | ||
void setup() { | void setup() { | ||
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); //Set the LED pin as output | pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); //Set the LED pin as output | ||
| − | pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set button pin as | + | pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set button pin as input |
} | } | ||
void loop(){ | void loop(){ | ||
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);//Read the value from the buttonPin | buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);//Read the value from the buttonPin | ||
if (buttonState == HIGH) { | if (buttonState == HIGH) { | ||
| − | digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //If the button input signal is high, the LED will light | + | digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //If the button input signal is high, the LED will light up |
} | } | ||
else { | else { | ||
| Line 67: | Line 64: | ||
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); | pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); | ||
// pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set the button pin as input | // pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set the button pin as input | ||
| − | pinMode(buttonPin, | + | pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);//Set button pin as input |
} | } | ||
void loop(){ | void loop(){ | ||
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); | buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); | ||
| − | if (buttonState ==HIGH) | + | if (buttonState ==HIGH) |
{ | { | ||
| − | delay(200); | + | delay(200); //Short time delay for stabilization |
// delay(1000); //Long time press | // delay(1000); //Long time press | ||
| − | // if (buttonState == LOW) | + | // if (buttonState == LOW) //Check still is low |
| − | led=!led; | + | led=!led; //LED state flip |
} | } | ||
digitalWrite(ledPin, led); | digitalWrite(ledPin, led); | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===digitalRead() usage=== | |
| − | + | Read a pin's value and return HIGH or LOW. | |
| − | === | ||
| − | Read a | ||
==Result== | ==Result== | ||
| − | *Program | + | *Program 1: LED is on while button is pressed down. |
| − | *Program | + | *Program 2: Each time you press the button, the LED will turn on/off. |
==Video== | ==Video== | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:18, 12 September 2016
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
ContentsObjectiveThe first two lessons showed you how to use software to control the LED directly. If we add a button to control the LED light, then we can combine the use of both hardware and software. Previously, we used Microduino I/O port as the output to control the LED. So if we want to use a button, how would we monitor when it is pressed? In this lesson, we will use a button as an example to show how to use Microduino as an input. Equipment
Button
Experiment SchematicUsing the external pulldown method, when the button is unpressed, the input to D2 is "LOW". When pressed, it is "HIGH". Program
const int buttonPin = 2; // Define button input pin
const int ledPin = 11; //Define LED pin
int buttonState = 0; //Initialize the button value
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); //Set the LED pin as output
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set button pin as input
}
void loop(){
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);//Read the value from the buttonPin
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //If the button input signal is high, the LED will light up
}
else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); //LED goes out
}
}
const int buttonPin = 2; // Define button input pin
const int ledPin = 11;
int buttonState = 0;
boolean led; //Define LED as boolean(true or false)
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); //Set the button pin as input
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);//Set button pin as input
}
void loop(){
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
if (buttonState ==HIGH)
{
delay(200); //Short time delay for stabilization
// delay(1000); //Long time press
// if (buttonState == LOW) //Check still is low
led=!led; //LED state flip
}
digitalWrite(ledPin, led);
}digitalRead() usageRead a pin's value and return HIGH or LOW. Result
Video |