Difference between revisions of "MCookie-AudioPro"
From Microduino Wiki
(→Features) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:MCookie-AudioPro-rect.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Microduino-AudioPro]] |
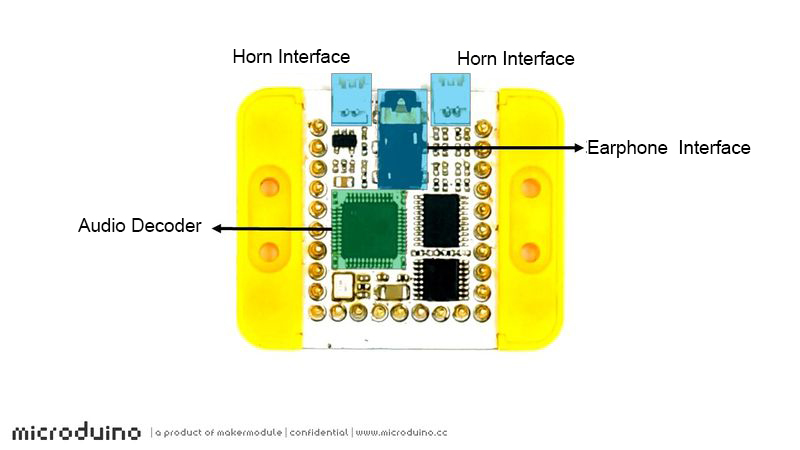
| − | Microduino AudioPro is a multi-function audio module with VS1053 as the decoder, and it integrates 2.2W stereo amplifier, and supports 2.5mm stereo headphone interface and MIDI function. | + | Microduino AudioPro is a multi-function audio module with VS1053 as the decoder, and it integrates 2.2W stereo amplifier, and supports 2.5mm stereo headphone interface and MIDI function. This module is usually used with the [[MCookie-SD|mCookie SD module]] to play music files. |
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Specification== | ==Specification== | ||
| − | *Support multiple formats of | + | *Support multiple formats of decoding: MP3/WMA/AAC/WAV/Ogg Vorbis/MIDI; |
| − | *Can real-time simulate as many as 128 kinds of MIDI instruments | + | *Can real-time simulate as many as 128 kinds of MIDI instruments: |
| − | **The universal MIDI and SP‐MIDI format 0 file can be played, and the format 1 and 2 file must be changed into format 0 by the players | + | **The universal MIDI and SP‐MIDI format 0 file can be played, and the format 1 and 2 file must be changed into format 0 by the players; |
| − | **The number of polyphony is 64 at most, and the number of continuous polyphony is 40 at most | + | **The number of polyphony is 64 at most, and the number of continuous polyphony is 40 at most. |
| − | + | *Integrate 2.2w stereo amplifier(LM4863): | |
| − | *Integrate 2.2w stereo amplifier(LM4863) | + | **Can control enabled through the GPIO4 of VS1053. |
| − | **Can control enabled through the GPIO4 of VS1053 | + | *2.5mm stereo headphone interface onboard; |
| − | *2.5mm stereo headphone interface onboard | + | *Head/extrovert automatically switching function; |
| − | *Head/extrovert automatically switching function | + | *18-bit-oversampling, multi-bit, and sigma‐delta high-precision DAC: |
| − | *18-bit-oversampling, multi-bit, and sigma‐delta high-precision DAC | ||
**Oversampling generally refers to the higher sampling rate more than nominal sampling rate for integral number of times, which is commonly used to improve the sampling accuracy. It means when restore the digital voice, use the sampling rate several times more than the nominal sampling rate to output, which can make the steps of the audio steep gently, and low the digital background noise and reduce the distortion, thereby get the high-quality audio superior to the output effect of the original sampling rate. | **Oversampling generally refers to the higher sampling rate more than nominal sampling rate for integral number of times, which is commonly used to improve the sampling accuracy. It means when restore the digital voice, use the sampling rate several times more than the nominal sampling rate to output, which can make the steps of the audio steep gently, and low the digital background noise and reduce the distortion, thereby get the high-quality audio superior to the output effect of the original sampling rate. | ||
| − | + | *SPI high-speed communication interface; | |
| − | *SPI high-speed communication interface | + | *Electrical characteristics: |
| − | + | **VS1053: 3.3V, 30~60mA; | |
| − | *Electrical characteristics | + | **LM4863: 5V, 1A. |
| − | ** | ||
| − | ** | ||
===Description of Pins=== | ===Description of Pins=== | ||
| − | *'''D2''' pin is the real-time MIDI interface | + | *'''D2''' pin is the real-time MIDI interface: |
| − | **The real-time MIDI is not enabled by default. If you need to enable it, just short connect the jumper on the back of the module | + | **The real-time MIDI is not enabled by default. If you need to enable it, just short connect the jumper on the back of the module; |
**After enabling the real-time MIDI, the baud rate of UART should be 31250bps, and at this time, SPI interface will not be available. | **After enabling the real-time MIDI, the baud rate of UART should be 31250bps, and at this time, SPI interface will not be available. | ||
:[[file:Micrduino-AudioPro-1Big2.jpg|800px|thumb|center|Microduino-AudioPro Spec]] | :[[file:Micrduino-AudioPro-1Big2.jpg|800px|thumb|center|Microduino-AudioPro Spec]] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 65: | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| − | *You can test the function through the _06_Microduino_AudioPlus_VS1053 | + | *You can test the function through the _06_Microduino_AudioPlus_VS1053 library:'''[https://github.com/wasdpkj/Microduino-IDE-Support/tree/master/arduino-ide-Support/%5B1.6.x%5D-hardware(library)/hardware/Microduino/avr/libraries/_06_Microduino_AudioPlus_VS1053 github]'''; |
| − | *Related example programs to download:'''[https://github.com/wasdpkj/AudioPro_VS1053/ github]''' | + | *Related example programs to download:'''[https://github.com/wasdpkj/AudioPro_VS1053/ github]''': |
| − | **Thereinto, '''Audio_MIDI''' is the example program of SPI interface realizes the real-time MIDI through loading the patches | + | **Thereinto, '''Audio_MIDI''' is the example program of SPI interface realizes the real-time MIDI through loading the patches; |
**Thereinto, '''Audio_ROM''' is the example program of playing audio files in ROM. | **Thereinto, '''Audio_ROM''' is the example program of playing audio files in ROM. | ||
| − | *You can see the MIDI material in the attachment | + | *You can see the MIDI material in the attachment; |
| − | *Tool for the hexadecimal to audio files:'''[[File:DataToHex.zip]]''' | + | *Tool for the hexadecimal to audio files:'''[[File:DataToHex.zip]]'''. |
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 105: | ||
*This table is reproduced inverted below, i.e. with high pitch at the top. | *This table is reproduced inverted below, i.e. with high pitch at the top. | ||
*To convert from any frequency to pitch (i.e. to the nearest note and how far it is out of tune, go to the frequency to note converter written by Andrew Botros. | *To convert from any frequency to pitch (i.e. to the nearest note and how far it is out of tune, go to the frequency to note converter written by Andrew Botros. | ||
| − | *How to do the | + | *How to do the calculation? Suppose that two notes have frequencies f1 and f2, and a frequency ratio of f2/f1. An octave is a ratio of 2:1, so the number of octaves between f2 and f1 is |
**no = log2(f2/f1). | **no = log2(f2/f1). | ||
Latest revision as of 03:21, 4 August 2017
|
Microduino AudioPro is a multi-function audio module with VS1053 as the decoder, and it integrates 2.2W stereo amplifier, and supports 2.5mm stereo headphone interface and MIDI function. This module is usually used with the mCookie SD module to play music files.
ContentsFeatures
Specification
Description of Pins
Documents
Development
ApplicationFAQHistoryGalleryVideoAttachmentMIDI numbers,Note names and frequenciesYou can refer to:NUSW
MIDI(GM1)
MIDI(GM1+GM2)
|