Difference between revisions of "The Use of Joystick Sensor"
From Microduino Wiki
(Created page with " {| style="width: 800px;" |- | ==Purpose== This tutorial will show you how to use Microduino Joystick. ==Equipment== *'''Microduino-CoreUSB''' *'''Microduino-Joystic...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | == | + | ==Outline== |
| − | + | Microduino-Joystick sensor is equipped with a two-way analog output interface. Its output values correspond to offsets on both the X-axis and Y-axis. It is small and beautiful. | |
| − | == | + | ==Specification== |
| − | * | + | *Electrical specification |
| − | * | + | **Analog input |
| − | * | + | **Output returned value 0-1,023 |
| − | * | + | *Tech parameters |
| + | **Detect displacement on both X- and Y-axis directions. | ||
| + | *Size | ||
| + | **Size of the switch: 17mm*17mm, | ||
| + | **Size of the board: 20mm*24mm | ||
| + | *Interface | ||
| + | ** Pin Description: GND, VCC, signal 1 output, and signal 2 output which is the analog signal and needs to use analog interface to detect (A0-A7). | ||
| + | **Y-axis corresponds to signal 1 output and the Y-axis corresponds to signal 2 output. | ||
| + | [[File:Joystick-line.jpg|center|400px]] | ||
| + | ==Development== | ||
| + | ===Equipment=== | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Module||Number||Function | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[mCookie-CoreUSB]]||1||Core board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[mCookie-Hub]]||1||Sensor pin board | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Microduino-Joystick]]||1||Joystick sensor | ||
| + | |} | ||
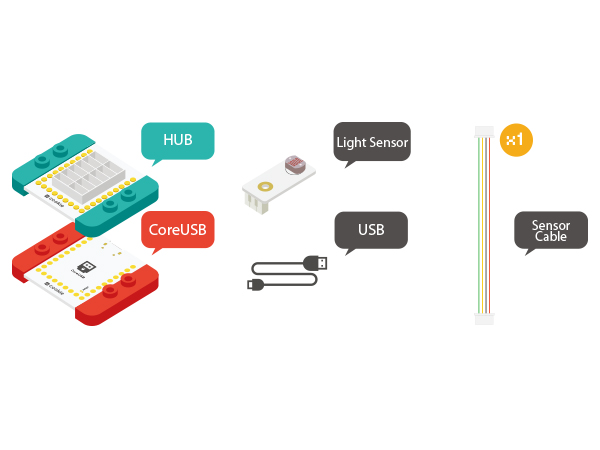
| + | *Other Hardware Equipment | ||
| + | **One USB cable | ||
| + | [[File:module-light.jpg|600px|center]] | ||
| − | * | + | ===Preparation=== |
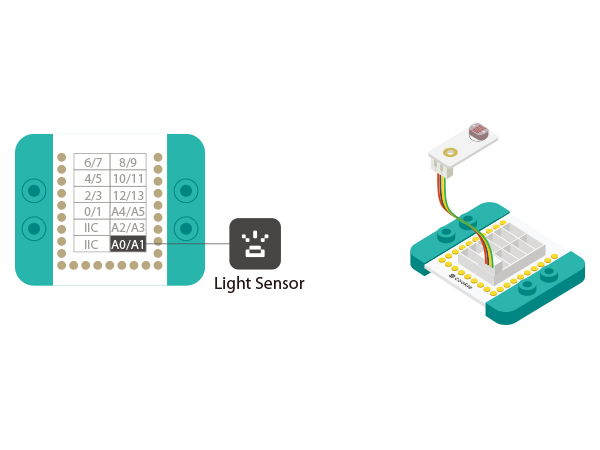
| − | * | + | *Setup 1:Connect Microduino-Joystick and the Hub 's A0 and A1 analog ports. |
| + | [[file:mCookie-pir-sensor.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
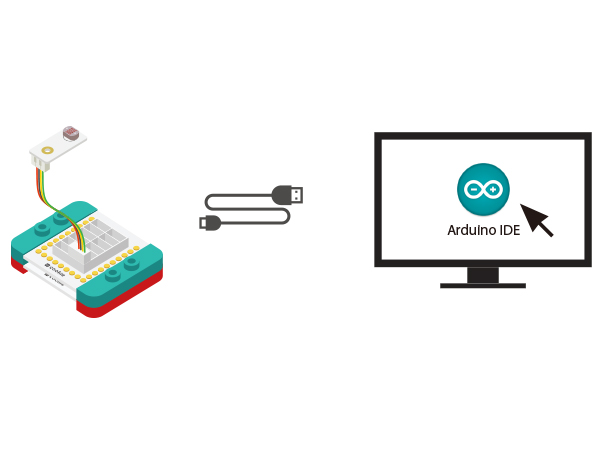
| + | *Setup 2:Stack the CoreUSB, Hub and Light together and then connect them to the computer with a USB cable. | ||
| + | [[file:mCookie-Light-pc.JPG|600px|center]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Experiment: Detect Analog Brightness Value === |
| − | + | *Open Arduino IDE and copy the following code into IDE. | |
| + | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
| + | #define Pin_X A1 | ||
| + | #define Pin_Y A0 | ||
| − | + | void setup() { | |
| + | Serial.begin(9600); //Serial initializing | ||
| + | pinMode(Pin_X,INPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(Pin_Y,INPUT); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | void loop() { | |
| + | int sensorValueX = analogRead(Pin_X); //X-axis input | ||
| + | int sensorValueY = analogRead(Pin_Y); //Y-axis input | ||
| + | Serial.print("ValueX:"); | ||
| + | Serial.print(sensorValueX); | ||
| + | Serial.print(","); | ||
| + | Serial.print("ValueY:"); | ||
| + | Serial.println(sensorValueY); | ||
| + | delay(100); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
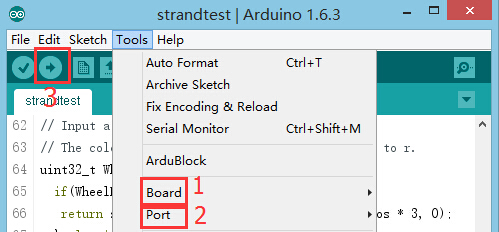
| + | * Select the right board from Tools→Serial Port in Arduino IDE and download the program. [[file:upload.JPG|500px|center]] | ||
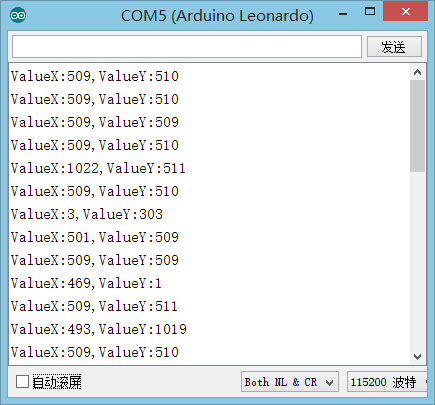
| + | * After the download, you can open the serial monitor. The displayed note reflects the current displacement analog values on both X-and Y-axis. | ||
| + | [[file:mCookie-pir-res.JPG|500px|center]] | ||
| + | *Result | ||
| + | **The right shift value decrease on the X-axis, close to zero while the left shift value increases and gets close to 1,023. | ||
| + | ** The top shift value decrease on the Y-axis, close to zero while the downward shift value increases and gets close to 1,023. | ||
| + | ===Program Debugging=== | ||
| + | *Use“analogRead(XX);” to read sensor's input analog value and judge the displacement on both the X-axis and Y-axis. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Application== |
| − | + | *To control object movement in two-dimensional space. | |
| − | + | *Game joystick | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Video== | ==Video== | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 07:08, 4 November 2015
ContentsOutlineMicroduino-Joystick sensor is equipped with a two-way analog output interface. Its output values correspond to offsets on both the X-axis and Y-axis. It is small and beautiful. Specification
DevelopmentEquipment
Preparation
Experiment: Detect Analog Brightness Value
#define Pin_X A1
#define Pin_Y A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Serial initializing
pinMode(Pin_X,INPUT);
pinMode(Pin_Y,INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValueX = analogRead(Pin_X); //X-axis input
int sensorValueY = analogRead(Pin_Y); //Y-axis input
Serial.print("ValueX:");
Serial.print(sensorValueX);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ValueY:");
Serial.println(sensorValueY);
delay(100);
}
Program Debugging
Application
Video |