Difference between revisions of "Introduction to Mixly"
From Microduino Wiki
(→Blocks) |
(→Blocks) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Communicate | | Communicate | ||
| − | | | + | | Blocks for other forms of communication such as IR, I2C, SPI, etc. |
|- | |- | ||
| Storage | | Storage | ||
| − | | | + | | Blocks used for storage of data on a SD card (SD module needs) or on board EEPROM. |
|- | |- | ||
| Sensor | | Sensor | ||
| − | | | + | | Blocks used for reading from an ultrasonic range finder, DHT11, DS18B20 or GPS. (Respective modules required.) |
|- | |- | ||
| Actuator | | Actuator | ||
Revision as of 01:28, 1 February 2017
This guide provides an introduction to Mixly. A drag and drop programming software (IDE) for Microduino and Arduino boards.
Setup
Please follow the setup guide for Mixly before proceeding the rest of this guide.
Interface Layout
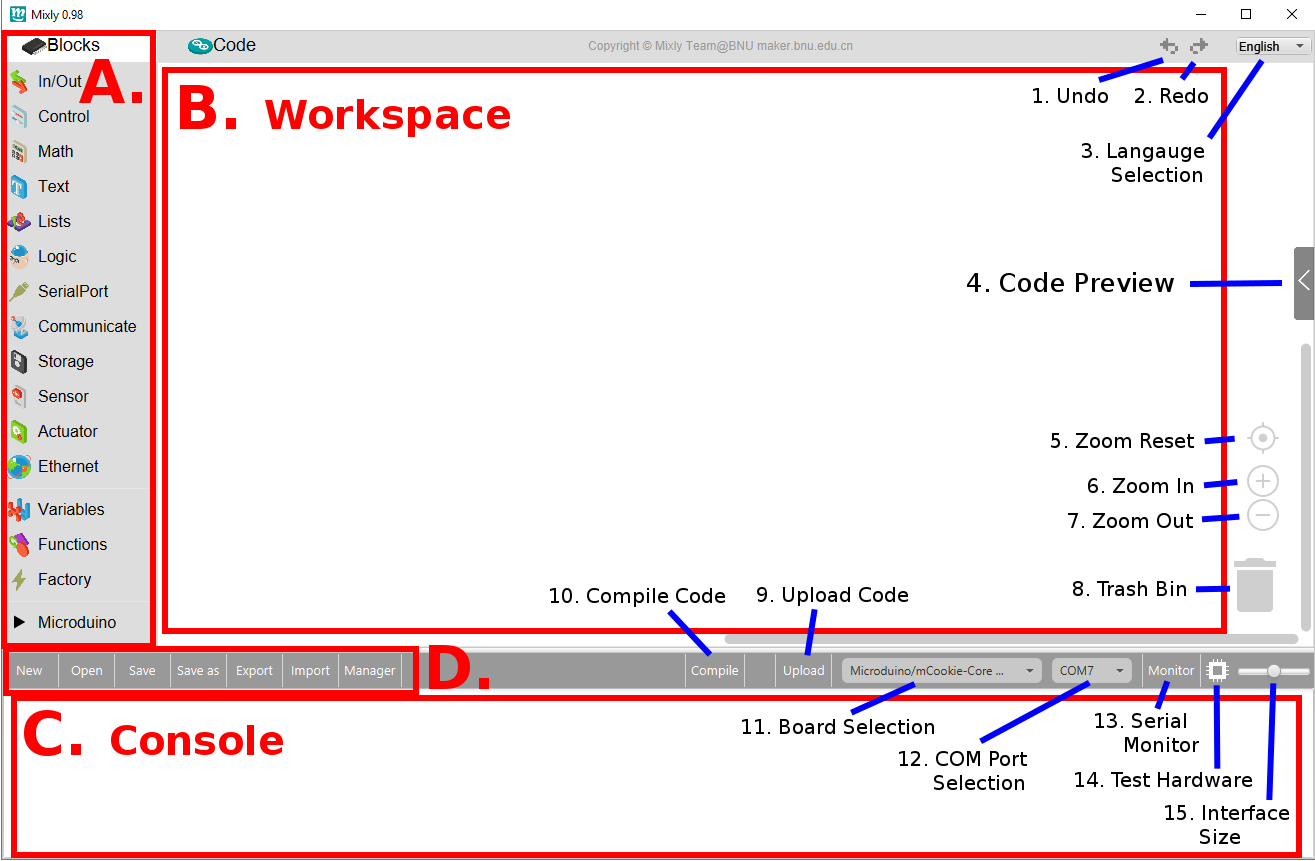
- Open Mixly by opening the mixly.jar.
- Section A. - Blocks.
- Section B. - Workspace.
- Section C. - Console.
- Section D. - File Options.
- 1. Undo - Reverts the last change.
- 2. Redo - Reverts the last undo.
- 3. Language Selection - Select the language of Mixly. Select-able languages are English, Spanish & Chinese
- 4. Code Preview - Opens a panel which shows the generated code from the Workspace blocks.
- 5. Zoom Reset - Resets the zoom to the default level.
- 6. Zoom In - Zoom in on the Workspace.
- 7. Zoom Out - Zoom out on the Workspace.
- 8. Trash Bin - Drag to the trash bin to delete blocks from the Workspace.
- 9. Upload Code - Compiles and uploads the code generated from the Workspace.
- 10. Compile Code - Compiles the code generated from the Workspace, but DOESN'T upload the code. Used to test if the code compiles without uploading it to a Core module afterwards.
- 11. Board Selection - Select the type of Core module/Arduino from this drop down menu that will be programmed.
- 12. COM Port Selection - Select the COM Port that the Core module/Arduino is connected to.
- 13. Serial Monitor - Opens the serial monitor that is used to send and receive data from the Core module/Arduino.
- 14. Test Hardware - Uploads a program to the attached board and tests to see if it is functional.
- 15. Interface Size - Scales the size of the interface of Mixly.
Blocks
Blocks are the pieces used to create code in Mixly. The blocks connects to each other if compatible. Incompatible blocks will not fit together. A program in Mixly is the collection of several blocks configured to perform a duty.
There are various types of blocks sorted into different categories. These include:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| In / Out | Blocks that controls the analog / digital pins on the Core module (or Arduino) boards. Such as digital write / read, analog write / read and interrupts. |
| Control | Blocks that determine the way the program executes. Such as if / else statements, delays, and loops. |
| Math | Blocks that provide mathematical functions such as arithmetic, trigonometric functions, etc. |
| Text | Blocks that provides text, text comparison, and text manipulation. |
| Lists | Blocks that creates lists and list accessing. |
| Logic | Blocks that are used for logically comparison. Such as equals, or/and and true/false. |
| SerialPort | Blocks to configure, use, and read / write to the Serial Port. |
| Communicate | Blocks for other forms of communication such as IR, I2C, SPI, etc. |
| Storage | Blocks used for storage of data on a SD card (SD module needs) or on board EEPROM. |
| Sensor | Blocks used for reading from an ultrasonic range finder, DHT11, DS18B20 or GPS. (Respective modules required.) |
| Actuator | |
| Ethernet | |
| Variables | |
| Functions | |
| Factory |