Difference between revisions of "The Use of Joystick Sensor"
From Microduino Wiki
(→Preparation) |
(Changed 1,023 value under 'Output returned' to 1023 for clarity) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Specification== | ==Specification== | ||
*Electrical specification | *Electrical specification | ||
| − | **Analog | + | **Analog Output from Sensor |
| − | **Output | + | **Output Value Returned: 0-1023 |
*Tech parameters | *Tech parameters | ||
**Detect displacement on both X- and Y-axis directions. | **Detect displacement on both X- and Y-axis directions. | ||
Revision as of 17:21, 28 July 2016
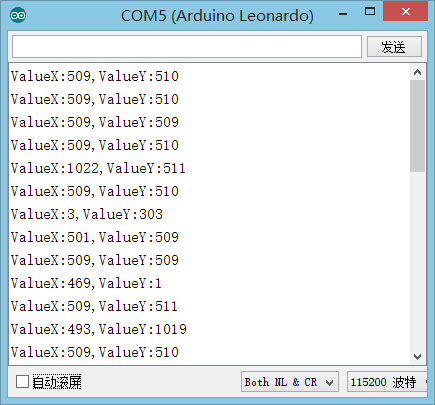
ContentsOutlineMicroduino-Joystick sensor is equipped with a two-way analog output interface. Its output values correspond to offsets on both the X-axis and Y-axis. It is small and beautiful. Specification
DevelopmentEquipment
Preparation
Experiment: Detect Analog Brightness Value
#define Pin_X A1
#define Pin_Y A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //Serial initializing
pinMode(Pin_X,INPUT);
pinMode(Pin_Y,INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValueX = analogRead(Pin_X); //X-axis input
int sensorValueY = analogRead(Pin_Y); //Y-axis input
Serial.print("ValueX:");
Serial.print(sensorValueX);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ValueY:");
Serial.println(sensorValueY);
delay(100);
}
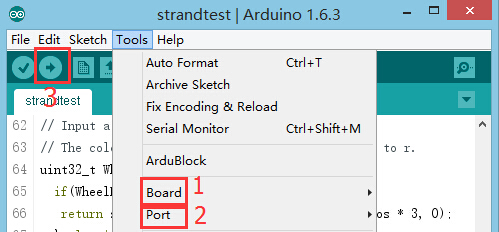
Program Debugging
Application
Video |