Difference between revisions of "Microduino-Module CoreRF"
(→Development) |
(→Development) |
||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
* Burn Microduino BootLoader | * Burn Microduino BootLoader | ||
**If the BootLoader fails, you need to use Arduino UNO or the other Microduino board to burn bootloader for the broken Microduino. | **If the BootLoader fails, you need to use Arduino UNO or the other Microduino board to burn bootloader for the broken Microduino. | ||
| − | **Users can refer to the tutorial: '''[[ | + | **Users can refer to the tutorial: '''[[Do you know how to use Arduino UNO to program bootloader to Microduino-Core?]]'''。 |
==Project== | ==Project== | ||
Revision as of 06:13, 15 May 2016
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
|
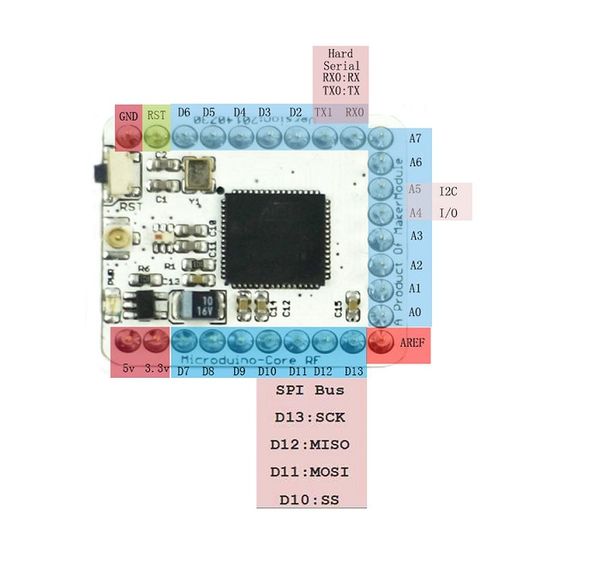
Microduino CoreRF is an AVR core board with 802.15.4 Wireless Protocol integrated. It supports any wireless modules based on 802.15.4 Protocol, including Zigbee, MAC/6LoWPAN and RF4CE. Contents[hide]Features
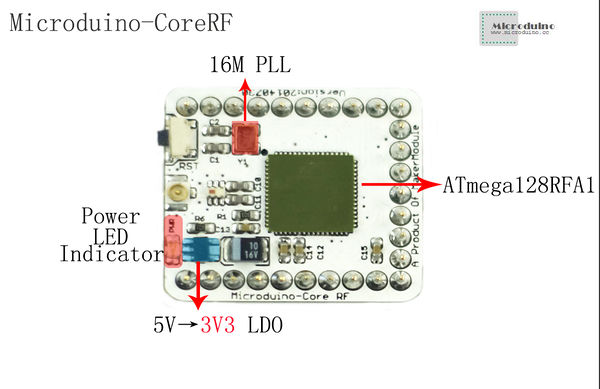
SpecificationAdopt ATmega128RFA1 core chip
Document
Schematic of CoreRF: 【CoreRF schematic diagram】
ATmega128RFA1: http://www.atmel.com/zh/cn/devices/ATMEGA128RFA1.aspx?tab=documents Development
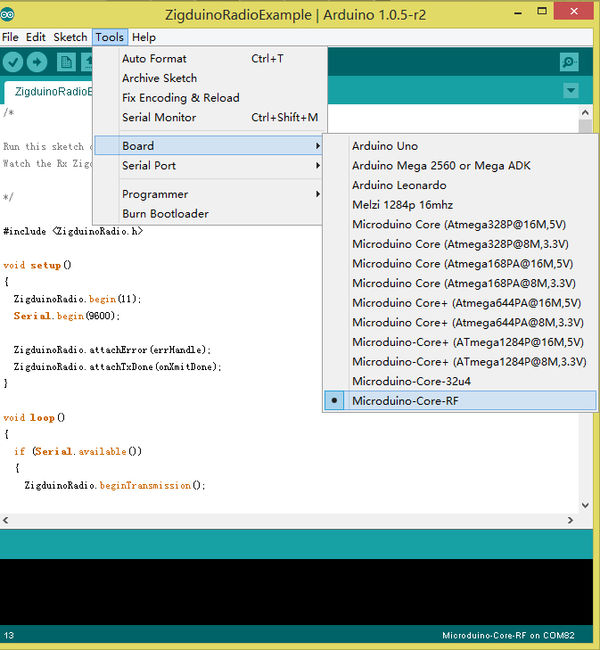
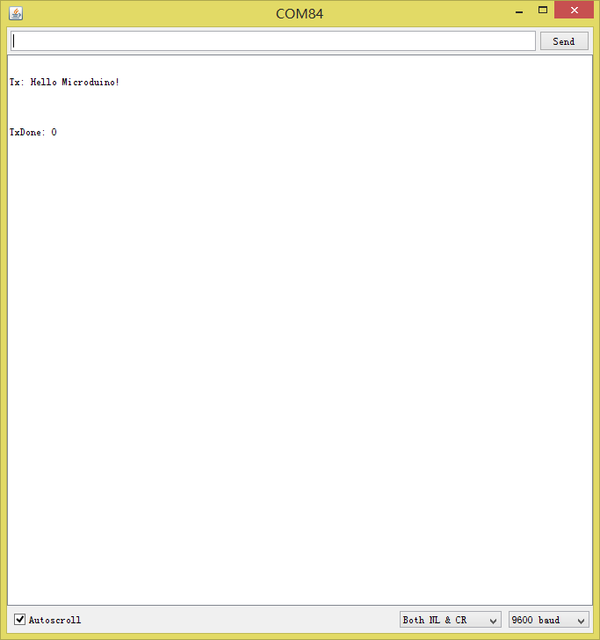
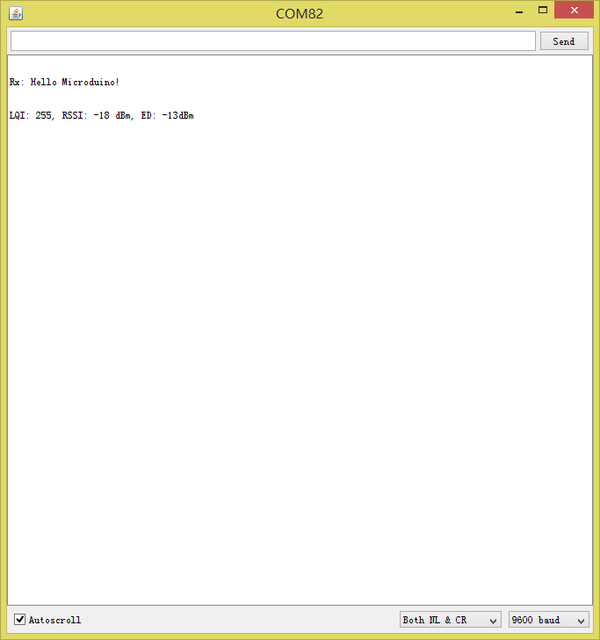
ProjectMicroduino-Quadcopter Tutorial TestUse program examples in ZigduinoRadio library to test. void loop()
{
if (Serial.available())
{
ZigduinoRadio.beginTransmission();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Tx: ");
while(Serial.available())
{
char c = Serial.read();
Serial.write(c);
ZigduinoRadio.write(c);
}
Serial.println();
ZigduinoRadio.endTransmission();
}
if (ZigduinoRadio.available())
{
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Rx: ");
while(ZigduinoRadio.available())
Serial.write(ZigduinoRadio.read());
Serial.println();
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.print(ZigduinoRadio.getLqi(), 10);
Serial.print(", RSSI: ");
Serial.print(ZigduinoRadio.getLastRssi(), 10);
Serial.print(" dBm, ED: ");
Serial.print(ZigduinoRadio.getLastEd(), 10);
Serial.println("dBm");
}
delay(100);
}
void errHandle(radio_error_t err)
{
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Error: ");
Serial.print((uint8_t)err, 10);
Serial.println();
}
void onXmitDone(radio_tx_done_t x)
{
Serial.println();
Serial.print("TxDone: ");
Serial.print((uint8_t)x, 10);
Serial.println();
}This example realizes wireless serial transmission function. Since the CoreRF adopts serial port download, you need firstly stack a Microduino-USBTTL on it: Choose Microduino CoreRF as the board card Open the serial monitor after uploading programs to the two Core-RF modules, input " Hello Microduino!", click "Send" and you'll get the following result: By here, we've completed the test. FAQPurchaseHistoryPicture
Video |