Clock
Contents[hide]ObjectiveThe course will show you how to use Processing to display a Microduino clock. Equipment
SchematicJust stack the three Microduino modules needed together ProgramReferring to ProcessingColock MicroduinoColock DebuggingStep 1: Build the hardware environment on the basis of the schematic, as follows:
The code of the two ends (Processing and Microduino) Microduino: //Just run the RTC module and transmit time data to the serial port void loop()
{
rtc.formatDate();
rtc.formatTime();
//send time data to port
Serial.print(rtc.getHour());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(rtc.getMinute());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(rtc.getSecond());
}
//Initialize time //initial time
void vosettime()
{
//rtc.initClock();
//day, weekday, month, century(1=1900, 0=2000), year(0-99)
rtc.setDate(4, 1, 6, 0, 14);
//hr, min, sec
rtc.setTime(15, 28, 50);
}
Processing: //Define the first serial data after getting it, and cache it if there is a new line // List all the available serial ports in the output pane. // You will need to choose the port that the Wiring board is // connected to from this list. The first port in the list is // port #0 and the third port in the list is port #2. println(Serial.list()); // Open the port that the Wiring board is connected to (in this case #0) // Make sure to open the port at the same speed Wiring is using (9600bps) port = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);
int radius = min(width, height)/2; secR = radius * 0.72; minR = radius * 0.60; hourR = radius * 0.50; clockDiameter = radius * 1.8; cx = width /2 ; cy = height /2 ; //Draw the current value after getting the x-coordinate value of the mouse via serial output void update(int x)
{
port.write(x);
stroke(255);
line(mouseX, 0, mouseX, 160);
text (mouseX, mouseX, 180);
}
//split data by ":"
String time[]=val.split(":");
//if some exception happend, initial time is 0 clock
try {
hour=Integer.parseInt(time[0]);
minute=Integer.parseInt(time[1]);
second=Integer.parseInt(time[2]);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
hour=0;
minute=0;
second=0;
}
//Draw a clock float s = map(second, 0, 60, 0, TWO_PI) - HALF_PI;
float m = map(minute+norm(second, 0, 60), 0, 60, 0, TWO_PI)- HALF_PI;
float h = map(hour+norm(minute, 0, 60), 0, 24, 0, TWO_PI * 2 ) - HALF_PI;
//draw clock
stroke(255, 250, 0);
strokeWeight(1);
line(cx, cy, cx + cos(s) * secR, cy + sin(s) * secR);
strokeWeight(2);
line(cx, cy, cx+ minR * cos(m), cy + minR * sin(m));
strokeWeight(4);
line(cx, cy, cx + hourR * cos(h), cy + hourR * sin(h));
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(255, 0, 0);
for (int a = 0 ;a<360;a+=6) {
float angle = radians(a);
float cx1 = (secR+20) * cos(angle);
float cy1 = (secR+20) * sin(angle);
point(cx + cx1, cy + cy1);
if (a%30==0) {
line(cx+cx1, cy+cy1, cx+cx1*0.98, cy+cy1*0.98);
fill(255);
int mark;
if (a/30>9) {
mark = a/30 -9;
}
else
{
mark = a/30 +3;
}
text(mark, cx+cx1*1.05-5, cy+cy1*1.05+5);
}
fill(90, 155, 11);
text(hour+":"+minute+":"+second, cx-25, cy+100);
text("Microduino", cx-25, cy-100);
}
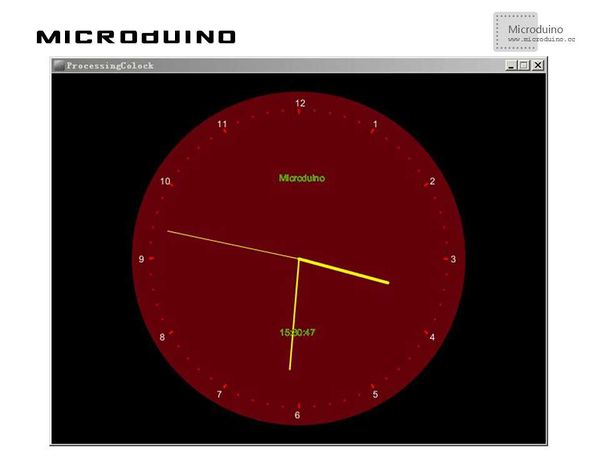
Step 3: Download the code and get it complied successfully. Step 4: Focus on Processing after the system goes well. ResultA running clock will be displayed on the screen, just like this
Video |