Difference between revisions of "Lesson 5--Microduino “LED Brightness and Potentiometer PWM”"
(→Program) |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Program== | ==Program== | ||
<source lang="cpp"> | <source lang="cpp"> | ||
| − | + | void setup() | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | pinMode(3,OUTPUT); //Choose the PWM output Port | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | void loop() | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | int val= analogRead(A0); //Read the analog port A0's value(voltage range is0-5V,corresponding value is 0-1204) | |
| − | + | val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 255); | |
| − | + | //Mapping the analog value(0~1024)to(0~255),the Max PWM value is 255。 | |
| − | + | analogWrite(3, val); | |
| − | + | //analogWrite(11,val/4); //The max PWM value is 255,so the analog value is divided by 4. | |
| − | + | } | |
</source> | </source> | ||
===map() function=== | ===map() function=== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
**toLow:Mapping range lower limit | **toLow:Mapping range lower limit | ||
**toHigh:Mapping range upper limit | **toHigh:Mapping range upper limit | ||
| + | |||
==Result== | ==Result== | ||
With the rotation of the potentiometer, LED brightness changes softly. | With the rotation of the potentiometer, LED brightness changes softly. | ||
==Video== | ==Video== | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 22 April 2014
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
ContentsObjectiveLast lesson we use the button to generate PWM to control the LED, this lesson we will use precision potentiometer to control the LED. The deffience between them is that the button use the digital voltage signal (0 and 1) to control which only has two states. When the signal changed,LED increases brightness by 5 units (0 ~ 255). Potentiometer use the analog voltage to generate PWM which is a linear change of state, so the LED's brightnees can be changed coherently and softly. Conversely,if use the button, you need consider the button shaking. Equipment
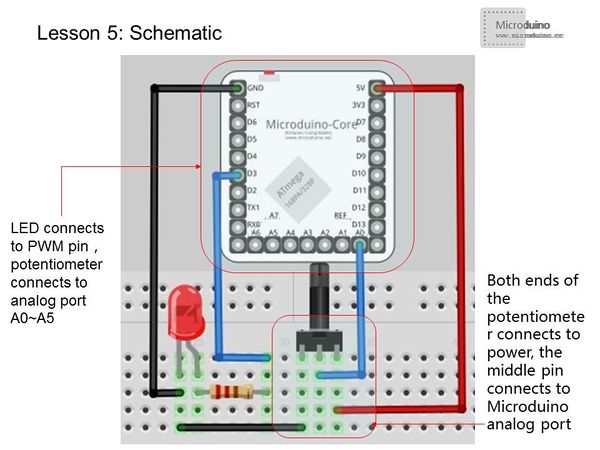
Experimental schematicConnection method, LED connects to the PWM output pin, and potentiometer connects to analog port A0 ~ A5. Analog interface can measure 0-5V voltage, and the corresponding return value is 0-1024, the measurement accuracy of the voltage variation is relatively high. Potentiometer had better choose winding precision linear potentiometer, because some cheap nonlinear potentiometer on the market doesn't have a good electrical characteristics. numerical drift is big which easy to cause the led flashing, Resistance is nonlinear variation, so the brightness change is not obvious, easy to produce the sense of hierarchy just like the button dimmer experiments, impact the test results. Programvoid setup()
{
pinMode(3,OUTPUT); //Choose the PWM output Port
}
void loop()
{
int val= analogRead(A0); //Read the analog port A0's value(voltage range is0-5V,corresponding value is 0-1204)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
//Mapping the analog value(0~1024)to(0~255),the Max PWM value is 255。
analogWrite(3, val);
//analogWrite(11,val/4); //The max PWM value is 255,so the analog value is divided by 4.
}map() function
ResultWith the rotation of the potentiometer, LED brightness changes softly. Video |