Difference between revisions of "Sensor-IO Split"
From Microduino Wiki
(→Introduction of Pins) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[File: Microduino-IO-split_rule1.jpg|600px|center]] | [[File: Microduino-IO-split_rule1.jpg|600px|center]] | ||
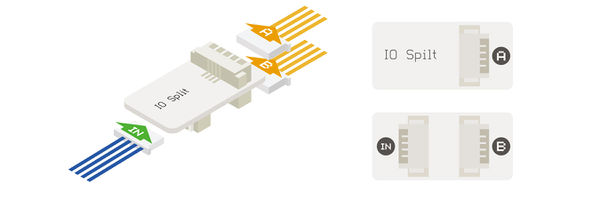
| − | After connecting the '''IN connector''' to a header on the Sensor Hub. | + | After connecting the '''IN connector''' to a header on the Sensor Hub. '''A interface''' corresponds to the '''even pins''' of header, and the '''B interface''' is corresponding to the '''odd pins''' header. |
For example, connecting to the 6/7 pin of Hub, the corresponding pin of A is 6, and the corresponding pin of B is 7. | For example, connecting to the 6/7 pin of Hub, the corresponding pin of A is 6, and the corresponding pin of B is 7. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:32, 12 April 2017
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
|
Sensor-IO-split can split a 4PIN interface (sensor / trinket connector) into two separate connectors. This gives access to the second GPIO on the standard sensor / trinket header. Introduction of Pins
After connecting the IN connector to a header on the Sensor Hub. A interface corresponds to the even pins of header, and the B interface is corresponding to the odd pins header. For example, connecting to the 6/7 pin of Hub, the corresponding pin of A is 6, and the corresponding pin of B is 7. Document
ApplicationIt can be used to divide the two IO signals of one 4PIN port in Sensor Hub into two 4PIN ports.
PurchaseGallery
|