Difference between revisions of "Open Source LED Dot Matrix Clock"
(→Outline) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
*Maker:peng | *Maker:peng | ||
*Introduction: | *Introduction: | ||
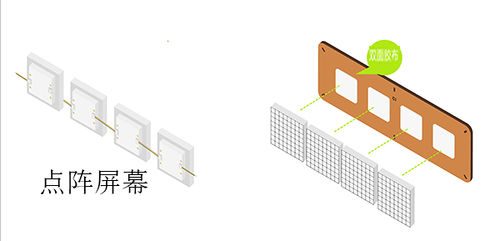
| − | **Cascade the four [[Microduino- | + | **Cascade the four [[Microduino-DotMatrix]] module. |
**Use a Bluetooth module to calibrate the time that the dot matrix displays through the mobile APP. | **Use a Bluetooth module to calibrate the time that the dot matrix displays through the mobile APP. | ||
**You can also send any character to dot matrix module to display through APP. | **You can also send any character to dot matrix module to display through APP. | ||
Revision as of 03:59, 26 April 2016
| Language: | English • 中文 |
|---|
ContentsOutline
Bill of Materials
Principle of the Experiment
Program Download
Programming
**Note:Please upload programs before stacking all modules together.
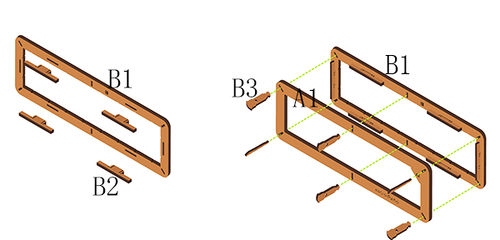
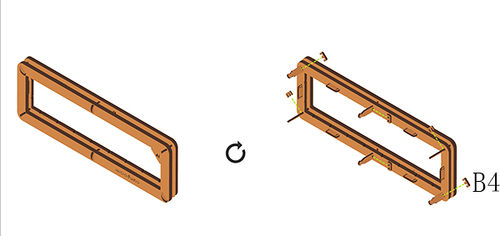
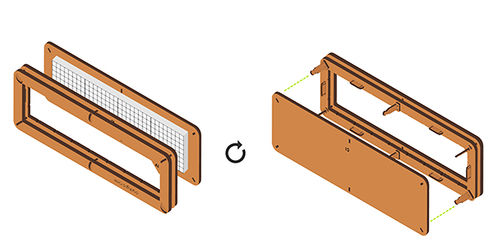
Installation
Operating Instruction
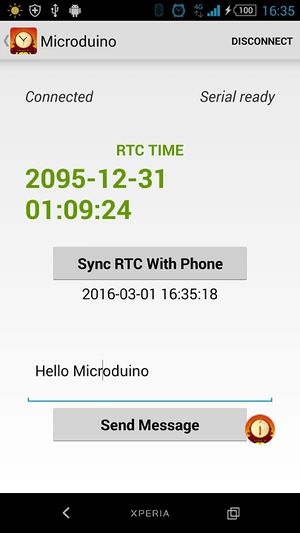
Bluetooth Connection
Display Text
Code InstructionCode to loading:File:Dot Maxtrix Clock.zip Dot Matrix Cascade uint8_t Addr[MatrixPix_X][MatrixPix_Y] = {
{ 64, 63, 62, 61}};
Define the IIC addresses of the four Dot Matrix modules as 64, 63, 62, and 61, and the arrangement type is 1x4. Bluetooth while (mySerial.available()) {...}
It is effective when there is a serial port data. mySerial.read() Red the data which is transferred by the UART. if (c == 't' && buffer_num == 0 && !buffer_sta_d)
buffer_sta_t = true;
if (c == 'm' && buffer_num == 0 && !buffer_sta_t)
buffer_sta_d = true;
Judge it is date or time data. strstr((char *)buffer, "t") Return the address where the "t" character first appears in buffer. sscanf((char *)strstr((char *)buffer, "t"), "t%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d", &sta[0], &sta[1], &sta[2], &sta[3], &sta[4], &sta[5]); From the address where the "t" character first appears in buffer, read the value according to the %d type, and write into sta[]. bleUpdata() Transfer data through UART, only by clicking the button on your mobile phone to send the specified character. If loosing, it will send character“0”. So without press, it will always show time. RTCrtc.getDate(); rtc.getTime(); setTime(rtc.getHour(), rtc.getMinute(), rtc.getSecond(), rtc.getDay(), rtc.getMonth(), rtc.getYear()) Get the date and time data of rtc. rtc.setDate(day(), weekday() , month(), 0, year() - 2000); //day, weekday, month, century(1=1900, 0=2000), year(0-99) rtc.setTime(hour(), minute() , second()); //hr, min, sec Set by hour, minute, second, day, month, and year format. Displaydisplay.print(second() % 2 ? " " : ":"); The second flashes, after being used justify whether the second can be exactly divided by 2. If it can, show it. If not, don’t show. display.getDeviceAddr(a) Get the IIC address of the device. display.getWidth(),display.getHeight() Return the X,Y coordinates. display.setLedColor(x, y, random(0, 255), random(0, 255), random(0, 255)) Set the color of each LED randomly. display.clearDisplay() Clean up the screen. display.setColor(X,Y,Z) Set the color of the full screen X:Red Y:Green Z:Blue display.writeString("string", MODE, time ,z)
string:any string. MODE:MODE_H displays characters horizontally. /MODE_V displays characters vertically. time:The displayed time(the flow velocity of the characters on the screen). z:X/Y coordinate. Through reading the RTC color, display the specific values in the form of coordinates. FAQ
|