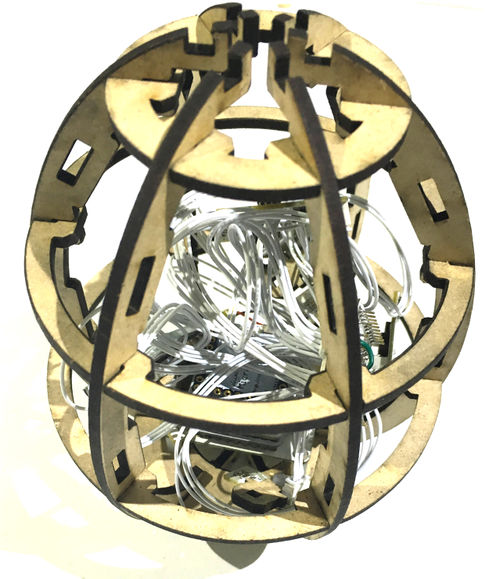
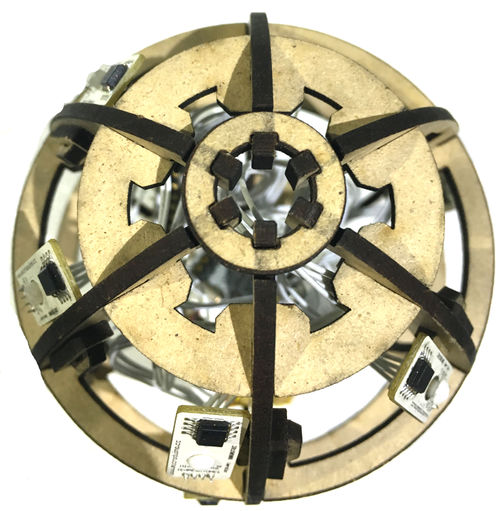
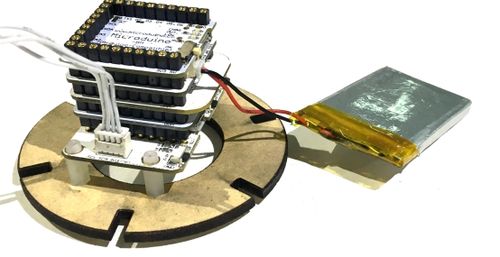
Open Source Smart Eggs Demo System
Contents[hide]Outline
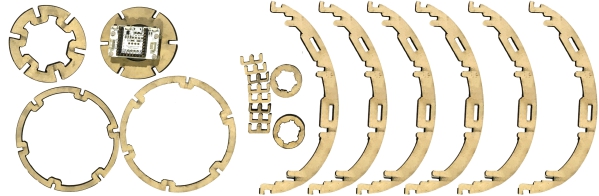
In this tutorial, we will use Microduino product module to build eggs temperature measuring system. This system is to gather the content of every points in the egg through temperature sensor, at the same time, send the data to mobile phone, and real-time produce temperature representation diagram. Bill of Material
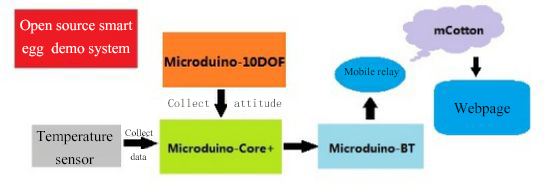
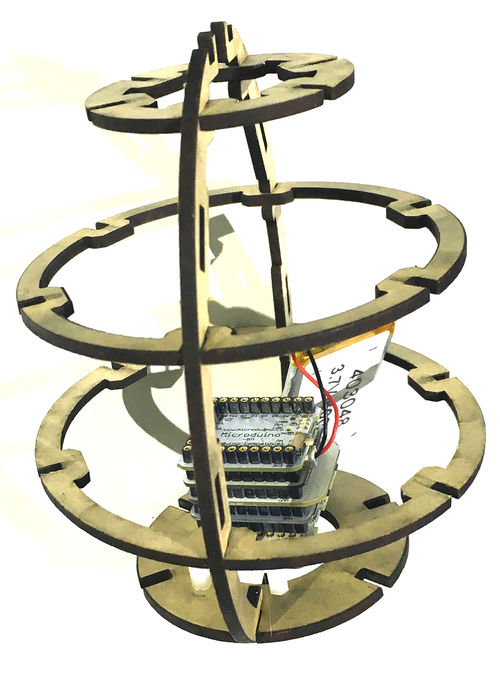
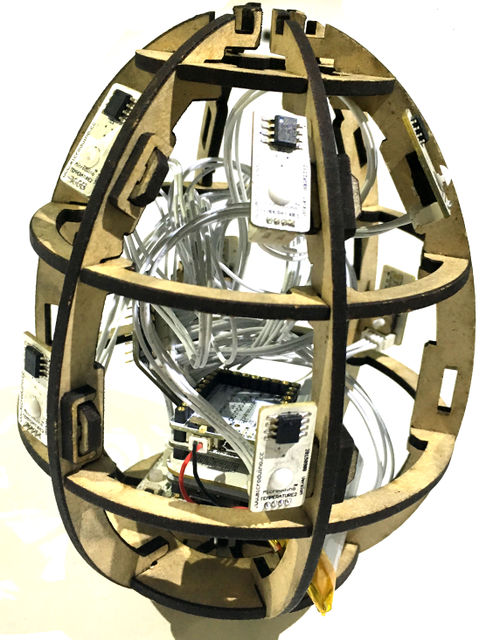
Principle of the ExperimentThe smart eggs system is mainly composed of two big parts. The data acquisition part is composed of 8 LM75 temperature sensor and a 10DOFmodule, real-time gather temperature of several points on the egg and the egg’s position and state, then link with the mobile phone through the procession of the core Core+ of the Bluetooth module Microduino-BT and send data to the mobile phone relay, then send to our cloud server mCotton, and then you canview temperature representation diagram and the egg’s attitude representation diagram through webpage.
Microduino-LM75 Microduino-Module Motion DocumentThe code of the egg:【Egg demo system code】 The code of the egg Github:SmartEgg Debug ProcessOverlay Microduino-Core+ and Microduino-USBTTL together, and upload the completed program to Microduino-Core+ through Microduino-USBTTL with USB cable. Note:Please upload programs before stacking all module together. Open Arduino IDE programming software, click [File]->[Open], and select Microduino_Audio_ble\ SmartEgg.ino after opening the card speaker folder. Click "√", and program. Click [Tool], and choose the right board + processor + port. Click "→", and upload. Assembling
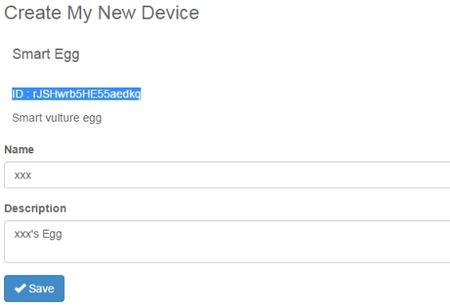
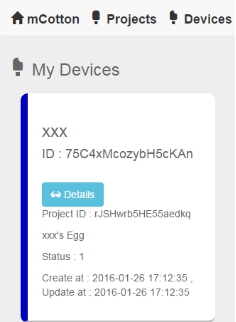
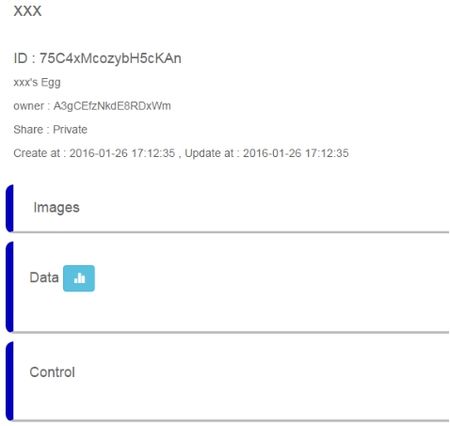
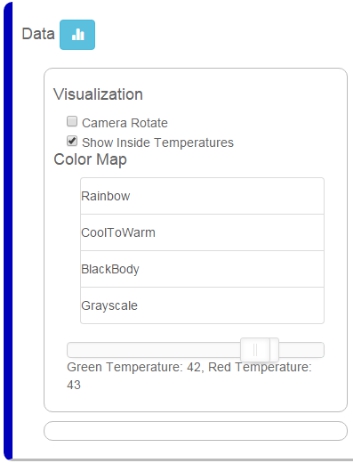
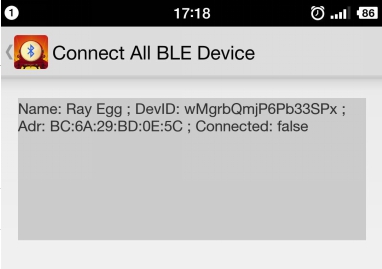
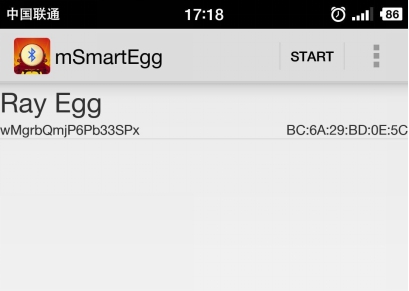
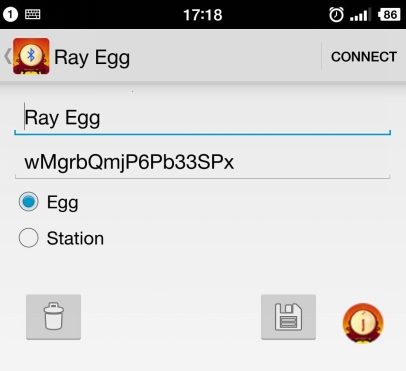
Now, the egg part assembly is finished. MCotton SettingEnter https://mcotton.microduino.cn/projects Click Sign in/Join at the top right corner, then click Create account at the bottom right corner in the drop-down list to create your own account. Input Email as your username and password, then click Create. After registration, it will automatically enter the login status. If not login, you should click Sign in at the top right corner to input username (email)and password to login in. After login, click Projects at the top left corner. At this time it will display a number of labels on this page. Find out Smart Egg label, and click Made It to enter the next page. Fill out your project name and project description here. You should keep the highlighted part in the picture in mind, and it is suggested to copy and save in a TXT. Then click √Save. Then enter myDevice page, you’ll see there appears a project named as XXX (the name you just set). Then click Details to enter a detail page. Click the blue icon on the right to Data to enter the page of data observation in the next page. If connect successfully, the egg data graph will be displayed on the right side, and the left part is option setting part. Mobile RelayClick the mobile phone APP to enter the following interface The picture will show the existing project information, and the Connected is the communicating state between the mobile phone and mCotton, and the following true/false is the link state between the egg and the mobile phone Bluetooth. Then click the Start button at the top right corner to enter the next step, at this time click the button at the top right corner, and choose Add Device. Input the name and program ID which is recorded in the mCotton step, then click the CONNECT button at the top right corner. Now the setting of the mobile phone relay part is completed. All steps have been completed. Watch that whether the state of the phone relay part is Connect,true or not. If it is, you can begin to observe web pages to observation data. Operating InstructionProgram Description#include <Wire.h>
#include <I2Cdev.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
#include <lm75.h>
SoftwareSerial bleSerial(4, 5);
TempI2C_LM75 termo[8] = {TempI2C_LM75(0x48, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x49, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4A, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4B, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4C, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4D, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4E, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits),
TempI2C_LM75(0x4F, TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits)
};
Quaternion q;
MPU6050 mpu;
uint8_t mpuIntStatus;
uint16_t packetSize;
uint16_t fifoCount;
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO memory buffer.
float buff1[10]; //Send data cache.
unsigned long time_mpu, time_tem;
uint8_t devStatus;
//To obtain a quaternion.
void dmpGetQuaternion()
{
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
if((mpuIntStatus & 0x10) || fifoCount == 1024)
{
mpu.resetFIFO();
}
else if(mpuIntStatus & 0x02)
{
while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize);
fifoCount -= packetSize;
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
// mpu.resetFIFO();
}
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
bleSerial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
mpu.initialize();
Serial.println("Testing device connections...");
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? "MPU6050 connection successful" : "MPU6050 connection failed");
Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP..."));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
if(devStatus == 0)
{
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
}
else
{
while(1)
{
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
}
}
}
void loop()
{
dmpGetQuaternion();
if(millis() > time_mpu + 1000)
{
time_mpu = millis();
buff1[0] = q.w;
buff1[1] = q.x;
buff1[2] = q.y;
buff1[3] = q.z;
/*
Serial.print("quat\t");
Serial.print(q.w);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(q.x);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(q.y);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(q.z);
*/
sendData(0xAA, 16, (uint8_t *)buff1);
}
if(millis() > time_tem + 5000)
{
time_tem = millis();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
buff1[i] = termo[i].getTemp();
Serial.print(buff1[i]);
Serial.print(",");
}
Serial.println(" ");
sendData(0xBB, 32, (uint8_t *)buff1);
}
}
void sendData(uint8_t cmd, int _num, uint8_t *_buf)
{
uint8_t sendBuf[40];
sendBuf[0] = 0xAA;
sendBuf[1] = 0xBB;
sendBuf[2] = cmd;
if(_num > 0)
memcpy(sendBuf + 3, _buf, _num);
sendBuf[_num+3] = 0x0d;
sendBuf[_num+4] = 0x0a;
bleSerial.write(sendBuf, _num + 5);
}video |